The oxygen sensor also called the O2 sensor or lambda sensor of the vehicle. It is a monitoring sensor. The o2 sensor operation is that the sensor measures the oxygen content in the exhaust manifold after the catalytic converter and reports it to the engine control unit of the vehicle. This information is then utilized to optimize the air fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
The oxygen sensor can get corroded, gets faulty the sensor response doesn’t match the actual amount of oxygen in the exhaust and you need to test the o2 sensor to verify the proper functioning of the oxygen sensor. The OBD2 scan tool will also provide you with detailed information on any troubled o2 sensor code that makes the oxygen sensor malfunction. If the oxygen sensor is bad, it can lead to an increase in harmful emissions.
This specific sensor is also responsible for bad fuel economy and engine performance issues, In case, the o2 sensor fails, the check engine light will also turn on. Regularly taking your car to the technician for maintenance and inspections is crucial to ensure that all the systems and the components of the car are working properly. In this powerful guide, you will quickly learn how to test a 4 wires o2 sensor with multimeter.
Related Post: Oxygen Sensor In A Car, How It Works, & Construction
How To Test A 4 Wire O2 Sensor With A Multimeter

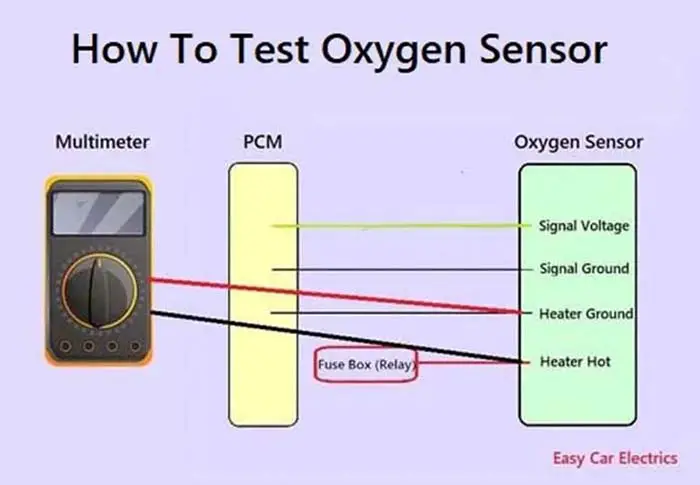
The oxygen sensors could have any number of wires ranging from one wire to four wires. The oxygen sensors with 1 or 2 wires are non-heated or unheated oxygen sensors whereas the oxygen sensors with 3 or 4 wires are heated oxygen sensors.
The o2 sensor with 4 wires connected to it, is the most commonly used oxygen sensor. Two wires are for the heated circuit and the other two wires are for sensing elements. They work by producing their very own voltage by increasing the temperature of the sensor to create optimal operating temperature.
Titania oxygen sensors are also very common nowadays. A zirconium bulb is placed on the tip of the oxygen sensor sitting in the exhaust. The bulb is coated with platinum inside out acting as its connector electrodes.
The inside of the bulb is vented and the outside is exposed to hot gases in the exhaust. The voltage is caused by the difference in oxygen level between the bulb and the oxygen in the air. If the air-fuel ratio is lean, the voltage reading generated would be low around 0.1 volts representing a high amount of unburned oxygen, whereas if the air-fuel ratio is rich, the voltage generated would be high around 0.9 volts and fuel consumption would be more.
Testing O2 sensor to ensure proper function of your vehicle’s emissions system. Below is the step-by-step procedure for testing your O2 sensors’ heater and signal wires with a multimeter.
Related Post: 4 Wire O2 Sensor Wiring Diagram
1. Oxygen Sensor Heater Wires Test
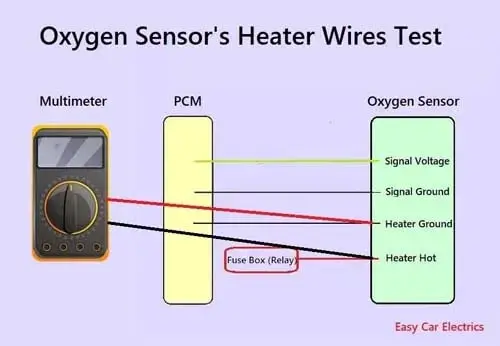
In this section, we will test the heater wire circuit of an oxygen sensor. First of all, you should check the oxygen sensor’s heater wires to see if the heating wires are broken. You can check this by the following method using a multimeter:
- Switch the multimeter to the Ohmmeter mode. Here we will back probe the oxygen sensor heater’s hot and ground wire.
- Connect the red lead of the multimeter to the heater hot wire
- And connect the black probe of the multimeter to the heater ground wire
- If the O2 sensor heater wires are functioning correctly, the readings on the multimeter should assume some value between 10 Ohms to 20 Ohms. If you have a bad o2 sensor or faulty o2 sensor the reading would be out of this range and should be replaced with a different o2 sensor.
Note: This test should be carried out when the engine of the car is switched off.
Related Post: Where Is Oxygen Sensor Located
2. Testing O2 Sensor Signal Wires Circuit
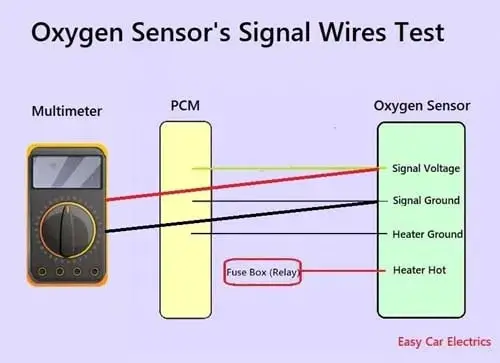
- Ensure that the engine of the car is cooled.
- Switch the multimeter to the voltmeter settings. Here we will back probe the o2 sensor’s signal voltage and ground wire.
- Connect the black lead of the multimeter to the ground signal wire.
- Connect the red lead of the multimeter to the signal voltage wire.
- Turn the engine of the car on.
- The oxygen sensor usually generates voltage somewhere around 0.1 to 0.9 volts.. If the sensor has failed, the sensor data would not be correct and it would be difficult to start the car and let it run.
If you don’t get readings similar to those shown above, you must get your car’s oxygen sensor diagnosed and repaired or you should take your car to the mechanic to replace it immediately as it is very vital for the correct air-fuel ratio in the combustion chamber of the car.
Factors That Can Affect O2 Sensor Testing
There are several factors that can affect the accuracy of an O2 sensor test. These include:
- Age And Condition Of The O2 Sensor: As the O2 sensor ages, it can become less accurate and may need to be replaced.
- Quality Of The O2 Sensor: Not all O2 sensors are created equal. Using a high-quality O2sensor can help ensure accurate test results.
- Environmental Conditions: Extreme temperatures, humidity, and altitude can all affect O2 sensor performance and testing.
- Vehicle Conditions: A variety of vehicle-related factors can affect O2 sensor testing, including fuel type, engine load, and exhaust system condition.
- Testing Equipment: It’s important to use properly calibrated and functioning testing equipment to ensure accurate O2 sensor test results.
- Technician Expertise: The experience and skill level of the technician performing the test can also impact the accuracy of the test results.
Are All 4 Wire O2 Sensors The Same?
When it comes to bad oxygen sensors, the type of sensor you have will make a difference in how you address the issue. All 4 wire oxygen sensors are not the same. The two common types of 4 wire O2 sensors are upstream sensors and downstream sensors. An upstream sensor is located before the catalytic converter while a downstream sensor is installed after it. Upstream sensors measure air-fuel mixtures while downstream ones measure emissions coming out of the catalytic converter itself.
While both types of sensors serve similar functions, they are designed to carry out different tasks so they cannot be replaced with one another on the same vehicle. If your car has an issue with either its upstream or downstream O2 sensor, then you need to replace that specific type for your vehicle to run properly again.
How Do I Test Bad O2 Sensor With A Multimeter
If you want to check if the sensor works fine or if sensor problems exist, you can easily learn how to check the oxygen sensor. Testing an O2 sensor with a multimeter is a simple process that can be done in a few steps. First, switch the multimeter to the ohmmeter mode and back pro be the heater wires. Then, connect the red lead of the multimeter to the heater hot wire and the black lead of the multimeter to the heater ground wire. When the engine is off, the readings on the multimeter should be between 10 Ohms and 20 Ohms.
Next, switch the Multimeter to the voltmeter settings and back probe the oxygen sensor’s signal voltage and ground wire. Connect the black lead of the Multimeter to the back probed ground signal wire and the red lead of the Digital Multimeter to the signal voltage wire. When the engine is on and warm up your car engine, the oxygen sensor voltage should cycle between 0.1 to 0.9 volts, indicating that the sensor wires are working properly. If not, then the oxygen sensor should be checked for rectification and repaired or the oxygen sensor must be replaced with a new one.
How Many Ohms Should An Oxygen Sensor Read
You can check the ohms on an O2 sensor by using a multimeter. First, switch the multimeter to the ohmmeter mode. Then, back probe the oxygen sensor heater’s hot and ground wire and connect the red lead of the multimeter to the heater hot wire and the black lead of the multimeter to the heater ground wire. The readings on the multimeter should assume some value between 10 Ohms to 20 Ohms. If the readings are outside of this range, the O2 sensor may need to be replaced.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
If you use the wrong O2 sensor, it can cause your car to run lean or rich. Lean means that there is not enough fuel being delivered to the engine, and rich means that too much fuel is being delivered. Either way, using the wrong O2 sensor can lead to engine damage.
The oxygen sensor is equipped with a fuse for the heater circuit. If the fuse is blown, the heater will not heat up the sensor and the sensor will not be able to properly measure the oxygen content of the exhaust gases.
Sign Up




