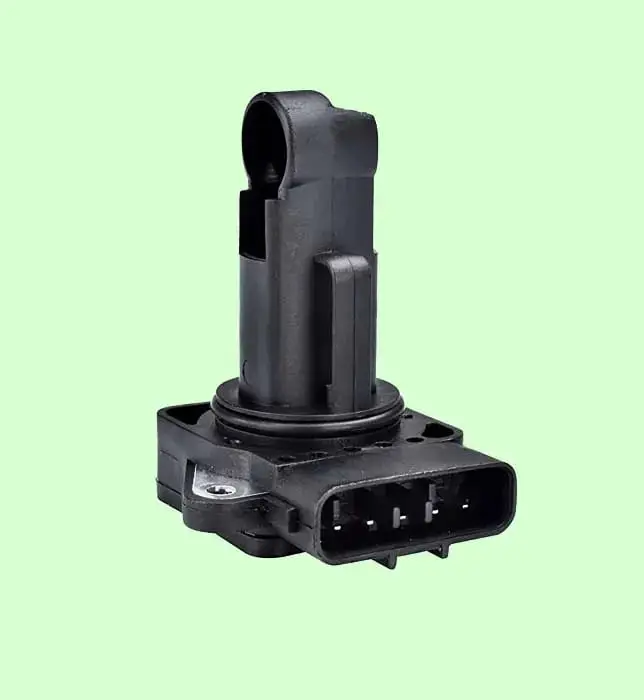
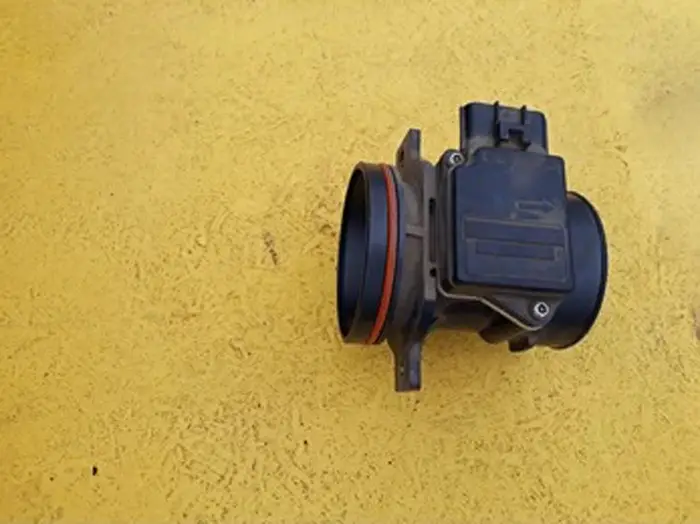
Cars with Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) systems have a mass airflow sensor, which is one of the most important parts of determining the precise air-fuel ratio.
Modern cars have several sensors controlling all the operations of engine and body components and indicating the malfunctions (if any) to the drivers so that they make take corrective actions and save their car from any severe damages.
Below we will cover some of the important questions regarding mass air flow sensors. In this powerful guide, you will learn what a mass air flow sensor is, its location, working, and function in easy-to-understand language.
Related Post: How To Clean Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
What Is Mass Air Flow Sensor

Mass Air Flow sensor also called MAF sensor is an electronic sensor, which measures the quantity of air going to the engine in a fuel-injected internal combustion engine.
Here mass means quantity, as its name defines a mass air flow sensor means a sensor that measures the Quantity Of Air flowing to the engine and then converts it into a voltage value. This output voltage value is proportional to the incoming air.
As we know that air is necessary with fuel for combustion in the engine cylinder. There is an air-to-fuel ratio for perfect combustion in a car engine called stoichiometric ratio, which is 14.7:1, which means for every 1 gram of fuel 14.7 grams of air is required, in which all the fuel is burned with no excess air.
Determining this exact amount of air for the perfect combustion is the job of the mass air flow sensor, where the ECU exactly knows how much air has entered the cylinder so that it lets the fuel enter the cylinder proportionally.
The MAF sensor works together with the oxygen sensor and determines a precise air-fuel quantity. Two types of mass airflow sensors are used in cars, a vane meter, and a hot wire. The vane-type airflow sensor measures the volume of the air entering the engine by a spring-loaded mechanical flap.
Related Post: The Risks Of Driving With Mass Air Flow Sensor Unplugged

In the latest cars, a hot-wire-based mass airflow sensor also has an intake air temperature sensor (IAT) installed in the MAF sensor that measures the temperature of the air passing through the engine. The hot wire MAF sensor measures the flow of air with a heated element, which is cooled by air flowing through it.
As the air cools the sensor, its current flow also changes and its internal circuitry then converts the current flow into an output voltage (proportional to the air coming through) called MAF Sensor Signal Voltage.
The amount of cooling is directly proportional to the flow of air. The higher airflow, the cooler the sensor gets, and vice versa.
When the sensor gets cooled, its resistance decreases, and the flow of current increases, which is interpreted by ECU as a high amount of air entered to the engine, so the ECU allows more fuel to the engine cylinder.
While a low airflow removes less heat, hence temperature and resistance of the sensor get high, so the flow of current decreases. The ECU interprets low current flow as less air entering the engine, so the ECU permits less fuel to the engine cylinder for combustion.
These flip-flop in current is converted to the proportional voltage by the integrated circuit present in the sensor and is sent to the ECU to determine the air-fuel ratio. These two indicators help the ECU to determine the amount of fuel required to be injected into the EFI system of a vehicle.
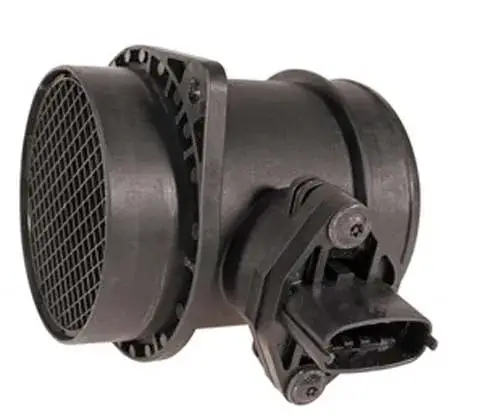

The mass air flow sensor is usually placed in the tube of air cleaning assembly between the air filter and the throttle body. It can be removed or replaced easily. Whenever required, just open the fastening screws from the air-cleaning assembly, remove the connector and take out the MAF sensor.
While removing it, take care that you do not disturb the wiring; otherwise there can be some electric issues with your car.
The main causes of malfunctioning of a MAF sensor are the dirt particles or road debris that comes inside along with the air passing through the engine. These either disconnect the heated wire or disrupt the electric supply. It is recommended to not drive a car with a malfunctioning MAF. It will slowly damage other components of the engine and it will also make your drive unsafe.
If a vehicle’s MAF sensor is not working properly, the engine will start sputtering or cranking and will not start. If anyhow, the vehicle is in running condition there will be a missing in its acceleration or it will feel under power.
It will also affect the fuel economy. These issues highlight the fact that how important a MAF sensor is in the air-cleaning assembly of your car.
Related Post: How To Reset Mass Air Flow Sensor
How Mass Air Flow Sensor Works
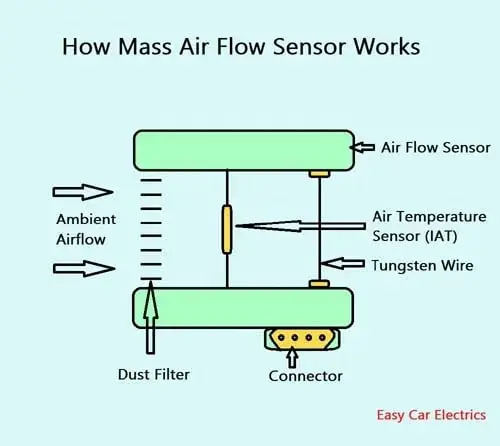
A mass airflow (MAF) sensor works on the principle of current flow to the wire and the amount of electricity required to keep it warm. A tungsten wire is used as an electrically heated wire to determine the mass of air flowing to the engine.
A dust cleaner, An intake air temperature sensor, and a tungsten wire are installed in the tube of the air cleaner assembly.
Related Post: 3, 4, & 5 Wire Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Wiring Diagram

When the ambient air passes through the air cleaner, the dust filter cleans the air, followed by the air temperature sensor, which measures the temperature of the air, and at last, the ambient air hits the tungsten wire.
A constant voltage is supplied to the tungsten wire to make it heated. So, when the air passes through the tungsten wire, it cools the tungsten wire, as a result, the resistance of the tungsten wire decreases, which increases the current flow of the tungsten wire.
Inversely, when less ambient air passes through the tungsten wire, less coolness is removed from the tungsten wire, and the resistance of the wire stays high, as a result, the current flow will be less.
As we know that resistance and current flow is inversely proportional, the lower the resistance, the higher the current flow, and vice versa. In the above explanation, the more the airflow, the cooler the tungsten wire gets, hence the more current will flow, and vice versa.
This high current flow of the tungsten wire is decoded by the ECU as a high airflow to the engine, while a less current flow is described as a lower airflow to the engine.
The ECU will use this current variation combined with the oxygen sensor to measure the intake of air in the engine of your car in order to calculate the air-to-fuel ratio and keep it optimum.
This is an Info
The denser air remove more heat from the heated tungsten wire, indicating a higher mass airflow.
Related Post: When & How To Clean Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
MAF Sensor Function

The basic function of a mass air flow sensor is to measure the rate of air flow that enters a car’s engine, which is necessary for the ECU to know how much fuel to inject into the cylinder.
It is an important component of the Engine Control Unit (ECU). The older models had a heated wire that switches off the engine after reaching a certain temperature. The newer ones do not have this burning-off function.
They rather have a film-like sensor or heat resistor which takes heat up to 120 to 180 °C. The intake of the air cools down it. The latest models of MAF sensors also have pulsations as well as return flow functions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Whether it is better to clean or replace a mass air flow sensor depends on the degree of contamination and the condition of the sensor. If the sensor is only mildly contaminated, then cleaning it may be sufficient. However, if the sensor is heavily contaminated or damaged, then replacing it may be necessary.
While a car can technically run without a mass air flow sensor, it will not run optimally. The mass air flow sensor is responsible for measuring the amount of air flowing into the engine so that the engine can adjust the fuel mixture accordingly. Without this sensor, the engine will run too rich or too lean, which can lead to decreased performance, increased fuel consumption, and potentially damage the engine.
Sign Up




