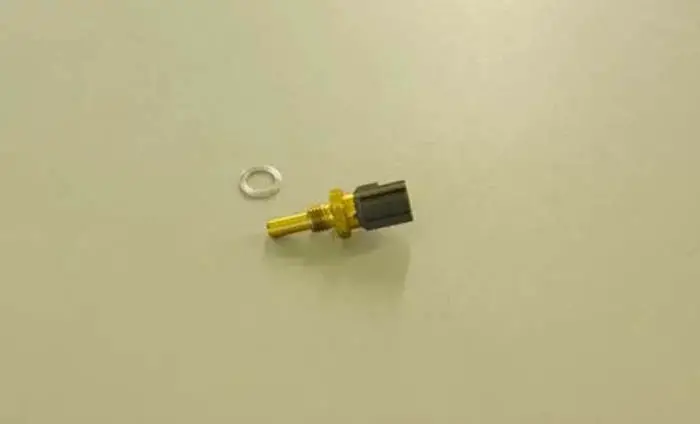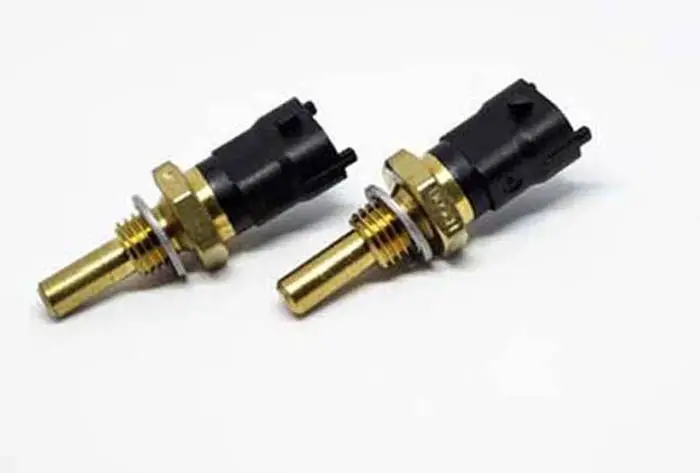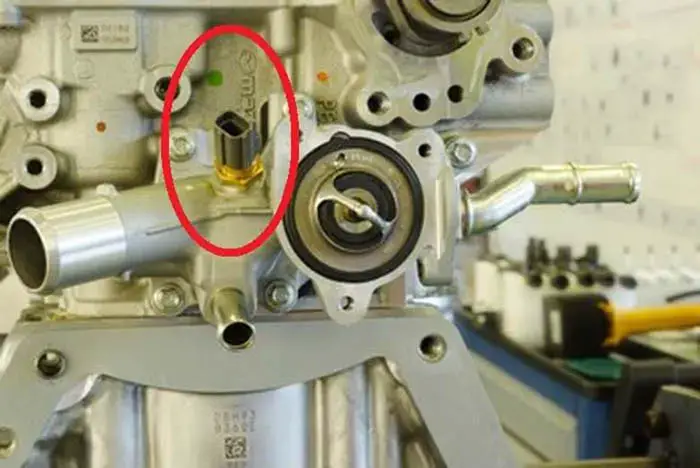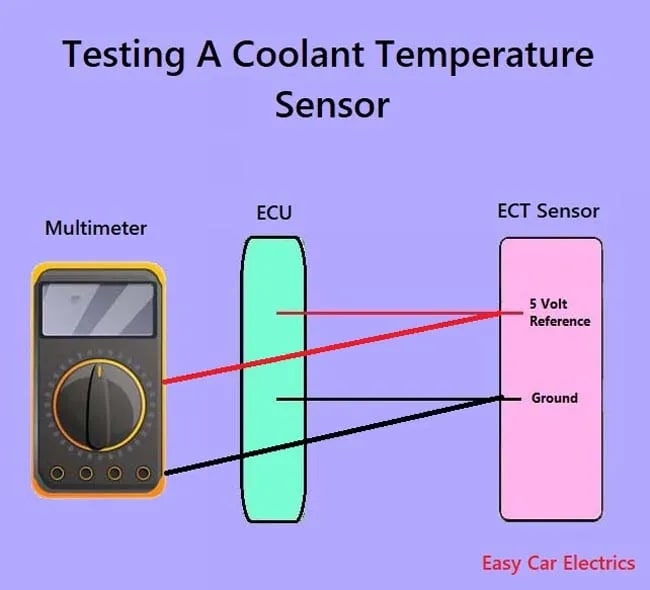
The Engine coolant temperature sensor is the sensor in the engine of the car, which is of the foremost importance in the car. It is used to measure the temperature of the engine indirectly by measuring the temperature of the engine coolant.
The engine coolant temperature sensor is a negative coefficient thermistor. Thermistors are resistors that change their resistance with the change in temperature. A negative coefficient thermistor is one whose resistance falls with rising temperatures.
The ECU of the car sends a signal to the ECT sensor; the sensor senses the temperature of the coolant and processes the received signal at that particular temperature. The sensor then sends the signal back to the ECU after processing it. Upon the arrival of the signal back at the ECU’s end, it determines the coolant temperature by noticing the change in the signal.
The temperature of the engine is determined based on the change in temperature of the coolant as it has absorbed the heat from the engine. This helps the ECU to determine the amount of fuel to be injected into the combustion chamber of the car to maintain the optimum temperature of the engine.
The ECT sensor stops working due to many reasons and needs to test to verify the proper functioning of the sensor. In this powerful article, you will learn how to test an engine coolant temperature sensor.
Related Post: Where Is The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Located
How To Test Coolant Temperature Sensor Wiring With Multimeter
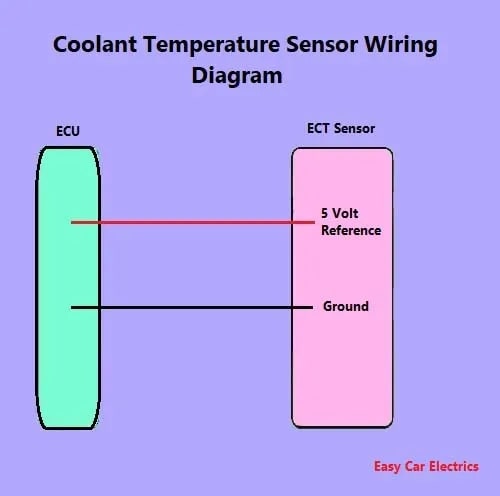
First of all, you have to locate the engine coolant temperature sensor of the car. When you open the hood of the car, you can find the ECT sensor in different locations depending on the make and model of your car.
It can be on the cylinder head of the car or could be mounted on the radiator outlet pipe. However, one of the most common locations of the ECT sensor is beside the thermostat housing.
Once you’ve located the ECT sensor you are all set to test it. The testing steps of the ECT goes as follows:
- Disconnecting the ECT sensor from the electrical connector.
- Measure the temperature of the surface of the engine using either a cooking thermometer or an infrared thermometer.
- Note the temperature reading of the surface of the engine.
- Set the Digital Multimeter to the resistance settings.
- Connect both wires to the connecting terminals of the ECT sensor and measure the resistance.
- Note the resistance of the ECT sensor along with the temperature and double-check the value of resistance from the service manual of the car.
- Then start the car’s engine.
- After two minutes note the temperature of the surface of the engine and the resistance of the ECT sensor’s resistance just like before.
- Note the values of the new resistance and temperature.
- Then after two more minutes again note the temperature of the surface of the engine and the resistance of the ECT sensor.
- After another two minutes again take the values of this pair and note them.
- After that, turn the engine off. Note the model of your ECT sensor.
- Compare the recorded readings of temperature and the respective resistance readings of the sensor from the service manual or from the internet for that particular model of sensor.
- Even if you don’t have the reference readings you can still know if your ECT sensor is working properly or not by noticing the change of resistance of the sensor with a change in the temperature of the surface of the engine. If the resistance decreases with increasing temperature then your ECT sensor is responding to the temperature changes as the ECT sensor is a negative coefficient thermistor.
This is an Info
The temperature of the engine surface should be measured near the ECT sensor.
Related Post: 9 Symptoms Of A Bad Engine Coolant Temp (ECT) Sensor
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The amount of time it takes for a car to reach operating temperature generally depends on the outside temperature. In colder weather, it can take up to 10-15 minutes for the engine to reach its ideal operating temperature, whereas in warmer weather it may only take 2-5 minutes. There are a few factors that contribute to this phenomenon, such as the thickness of the engine oil, the thermal conductivity of the materials used in the engine, and so on.
There is a common misconception that revving the engine will warm it up faster. This is not true. Revving the engine actually decreases the amount of time it takes for the engine to reach operating temperature. When you rev the engine, you are increasing the demand for heat from the engine. The engine responds by burning more fuel, which increases the rate of heat transfer from the combustion chamber to the cooling system.
The engine in a car is made up of many different parts, all of which need to work together in order for the car to run. The engine relies on a variety of chemical reactions to create the energy that powers the car. These reactions are most efficient when they are at a certain temperature. When the engine is cold, these reactions happen more slowly and less efficiently.
Sign Up