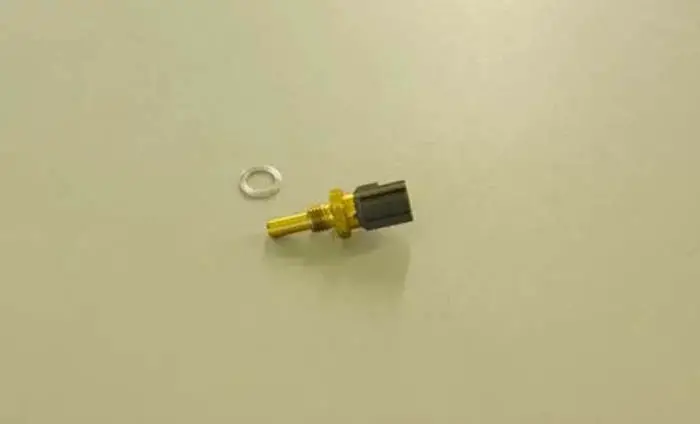
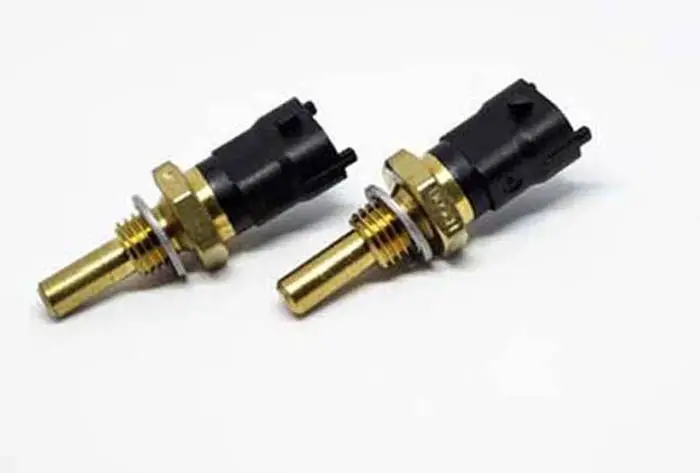
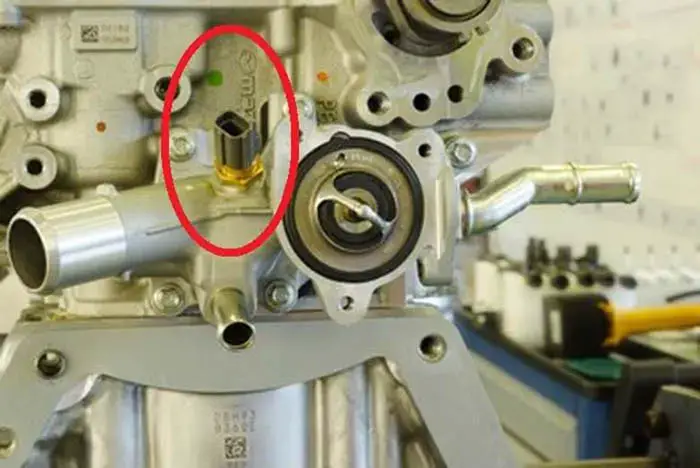
The Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor or the ECT sensor of your car is one of the most important sensors in your car, which assists the engine of the car functioning properly.
In a car consisting of an internal combustion engine, the cooling system also takes care of temperature changes and maintains the temperature of the car. This is mandatory as it prevents overheating, which can cause a lot of problems if overlooked.
In this powerful guide, you will learn what the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is, how it works, and its functions in easy-to-understand language.
Related Post: Where Is The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Located
What Is ECT Sensor

The Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) also known as the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor (ECTS) is a thermal resistor or thermistor used to measure the temperature of the engine’s coolant (antifreeze) and sends this information to the ECU.
Antifreeze (coolant) is a liquid that is mixed with water to keep the radiator from freezing or overheating in extreme weather conditions. As the car’s engine heats up, the heat is absorbed by the engine coolant, and its temperature rises.
This rise in temperature is sent to the ECU, which determines the temperature of the engine, and adjusts the amount of injection of fuel into the combustion chamber.
The ECT sensor of the car does not measure the temperature of the car’s engine directly; instead, it measures the temperature of the engine’s coolant and converts those measurements into electrical signals, which are then used to have the correct air-fuel ratio for combustion.
This reading of the temperature of the engine coolant determines the resistance of the ECT sensor; the voltage sent by the car ECU is then processed under this resistance and sent back.
The voltage reading sent back by the ECT sensor is then used to observe the amount of heat that the engine coolant has absorbed from the engine and determines the engine’s temperature using this recorded reading of the temperature of the engine’s coolant.
Related Post: How To Test Coolant Temp Sensor Wiring With Multimeter

According to the research, the ECT sensor has effects on the following elements.
- Air fuel ratio
- Engine cooling fan
- Idle air control
- EGR valve opening and closing
The coolant temperature sensor is a resistor-based (thermistor) sensor, which changes its value according to the change in temperature of the engine’s coolant.
The ECT sensor of the car is a thermistor mostly with a negative temperature coefficient and changes its temperature according to the temperature in its surroundings. The thermistor has two types of coefficients that determine its working mechanism.
- Positive Temperature Coefficients (PTC) Thermistor
- Negative Temperature Coefficients (NTC) Thermistor
In the positive temperature coefficient (PTC) thermistors, the resistance increases with the increase in the temperature, whereas for a thermistor with a negative temperature coefficient, the resistance of the thermistor decreases with the increase in temperature.
When a signal is sent by the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) of the car to the ECT sensor, the ECT sensor processes the received signal on its current resistance which is in fact a product of the temperature of the engine and sends it back to the ECU of the car.
If this signal, which is sent back by the ECT sensor, is out of range or is unexpected, due to the abnormal temperature of the engine, the ECU turns on the check engine light on your dashboard, so you know that your car’s engine is overheating.
The ECT sensor sends the signals to the ECU; the ECU continuously monitors engine temperature to make sure the engine is running under the right air-fuel mixture. In fact, the ECU sends more fuel to the engine, when it is cold, the fuel must be richer to prevent stalling and less fuel when warmed up.
The tip of the Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor is plugged into the path of the engine coolant in such a way that it is completely immersed in the engine coolant.
Related Post: How to Replace a Coolant Temperature
Coolant Temperature Sensor Function

The Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor is among the key management sensors that are installed in the hood of the car.
The function of the engine coolant sensor is to measure the temperature of the engine liquid coolant and convert it into an electrical signal then send it to the ECU to continually monitor the engine temperature. In other words, you can say, the engine’s coolant temperature sensor protects the engine from overheating.
The ECT sensor overall performs a major role in the key calculations of the air-fuel ratio, which is responsible for the proper functioning of the car and determines its performance of the car.
The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) uses these readings sent forward by the ECT sensor to adjust the amount of fuel to be injected into the combustion chamber and decides to turn ON and OFF the radiator fan and the ignition timing.
Related Post: Wire Coolant Temperature Sensor Wiring Diagram
How Does A Coolant Temperature Sensor Work

The Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor is similar to the IAT sensor in working, which is used to get an accurate measurement of the temperature of the engine.
The Engine Coolant Temperature sensor does this by getting a 5-volt reference from the car’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU). The ECT sensor is a thermal resistor whose resistance varies with the temperature of the engine coolant.
The voltage signal is sent back (by ground wire) to the ECU by the ECT sensor after applying the resistance. This voltage received by the ECU helps the ECU determine the change in temperature of the fluid and hence the heat absorbed by the fluid from the engine.
The ECU examines the voltage received back to it by the coolant temperature sensor, this voltage signal received back will tell the ECU about the current temperature of the coolant.
Then the ECU decides the amount of fuel to be injected, the fuel mix, the timing of ignition, and the state of the radiator fan. With the cold engine of 20 ºC ambient air temperature, the resistance of the ECT sensor is in the range of 2000Ω and 3000Ω.
After the engine has started, the ECT sensor’s temperature starts to increase, the resistance decreases proportionally. At 90 ºC its resistance decreases to 200Ω to 300Ω.
When the engine coolant temperature usually reaches 98 degrees celsius, the ECU orders the radiator fan to be turned ON by providing the earth signal to the radiator’s relay in the fuse box to cool down the engine coolant.
Related Post: 9 Symptoms Of A Bad Engine Coolant Temp (ECT) Sensor
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In a car, there are typically two coolant temperature sensors. One sensor is located in the engine block, and the other sensor is located in the radiator. The engine block sensor monitors the temperature of the engine coolant, and the radiator sensor monitors the temperature of the coolant as it flows through the radiator.
The coolant temp sensor does not control the fan. In modern cars, the fan is controlled by the engine management system, which uses input from the coolant temp sensor to determine when to turn the fan on. When the engine is running hot, the coolant temp sensor sends a signal to the engine management system, which then turns on the fan.
Sign Up