The air intake sensor or IAT sensor, full form is the intake air temperature sensor and is one of the most important parts of the engine’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU).
This is an essential sensor as it maintains a nice emission level and helps the engine to burn the fuel completely and not create any sulfur compounds and lessen the number of nitrogen oxides significantly.
In this powerful article, you are going to learn what the intake air temperature sensor is, its function, and working in easy-to-understand language.
Related Post: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Location
How Important Is Intake Air Temperature Sensor
The intake air temperature sensor is a key component in ensuring the proper functioning of an internal combustion engine. The sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the engine and provides this information to the engine control unit. The ECU uses the data from the intake air temp sensor to adjust the fuel injection and ignition timing. This helps to ensure that the engine is operating at peak efficiency and prevents knocking and pre-ignition.
If the Intake Air Temperature Sensor is not working, it can cause a number of problems. First, it can cause the engine to run too hot or too cold. Second, it can cause the engine to run lean or rich. Third, it can cause the engine to misfire. Fourth, it can cause the engine to stall. fifth, it can cause the check engine light to turn on. Finally, it can cause the engine to backfire. In short, it will decrease the efficiency of the engine, which can lead to decreased performance and fuel economy.
The Intake Air Temperature sensor is crucial to the effectiveness of your engine. In order to maintain optimal engine performance, it is important for the intake air temperature sensor to be functioning properly. This sensor helps to regulate the amount of air that enters the engine. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) will adjust the air-fuel mixture according to the feedback of the Intake Air Temperature Sensor in order to maintain optimal engine performance.
In conclusion, the intake air temperature sensor is a vital component to the proper function of a vehicle. Keeping your Intake Air Temperature in good working condition is essential for maximizing engine output when it comes to the performance of a modern engine. It helps the engine run smoothly and efficiently by providing accurate information about the temperature of the air entering the engine. If the sensor is not working properly, it can cause serious engine problems. It is important to have the sensor checked regularly to make sure it is functioning properly.
What Is Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor

The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor, Inlet Air Temperature Sensor, or Air Intake Sensor was labeled with different names before OBD2 (Pre 1995) such as Manifold Charging Temperature (MCT) Sensor, Manifold Air Temperature (MAT) Sensor, or a Charge Temperature Sensor (CTS),
The intake air temperature sensor senses the temperature of the air and sends it to the ECU of the engine. From this signal, the ECU decides the amount of fuel to be injected into the combustion chamber and the rate at which the spark should be provided to the air-fuel mixture.
The IAT sensor helps to measure the relative density of the air with the environment and helps the ECU in calculating the stoichiometric amount of fuel to be injected in the correct ratio.
The intake air temperature is a resistance-based sensor, which exchanges the temperature of the incoming air with the magnitude of resistance, and sends it to the car computer.
The IAT sensor uses a thermistor. A thermistor is an electrical resistor that changes its values according to the temperature around it. Thermistors have two types of coefficients that decide their working mechanism:
- Positive Temperature Coefficients (PTC) Thermistor
- Negative Temperature Coefficients (NTC) Thermistor
The Positive Temperature Coefficients (PTC) thermistors increase their resistance with a temperature rise, while the resistance of Negative Temperature Coefficients (NTC) rises with a decrease in temperature.
This change in resistance is detected by ECU in the return voltage from the IAT sensor (through a signal wire), and hence, it determines the air temperature.
Mostly, the IAT sensors are negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistors, which means the resistance decreases as the temperature of the sensor increases. A positive temperature coefficient (PTC) thermistor is rarely used these days.
As you know, these days, all cars are based on an electronic fuel injection system, in which the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber through the electronic system.
In an EFI system, you must have the correct air-fuel ratio to increase fuel efficiency. To have a correct air-fuel ratio, you need to know the temperature of the air. It is because colder air is denser than hot air. It uses more fuel due to having more oxygen molecules, which demands more fuel to maintain the correct air-fuel ratio.
So, the temperature of the air is measured by the intake air temperature sensor. The ECU takes the information from the IAT sensor and sends it to the computer for the perfect air-fuel ratio. This is very important as it helps the car’s engine to work properly on a cold day. It also helps your car to maintain fuel economy in hot weather.
Related Post: IAT Sensor Wiring Diagram
Function Of Intake Air Temperature Sensor
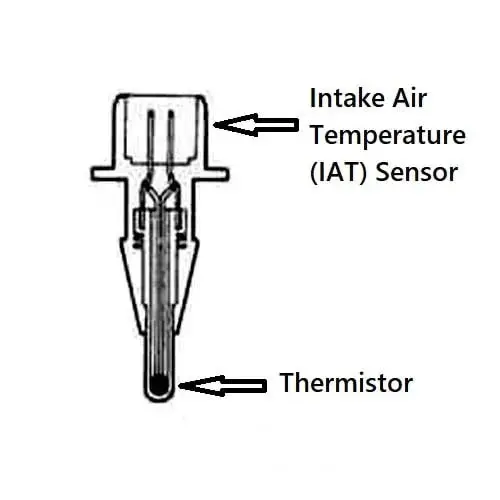
The Intake Air Temperature sensor is the heart of the Electronic Control Unit (ECU) of the car as it determines the efficiency of the combustion in the combustion chamber in the car.
The function of the IAT sensor of the car is to determine the temperature of the air at the intake manifold of the car and transmit the recorded temperature of the air to the ECU of the car.
This is necessary because a change in air temperature changes its density, which affects the number of oxygen molecules per unit area.
Cold air is denser and has more oxygen, which requires more fuel for complete combustion while warm air is lighter and has fewer oxygen molecules in the unit area, which demands a lower amount of fuel.
The computer of the car then uses this related data to calculate the correct stoichiometric amount of fuel to be injected into the combustion chamber for complete combustion of fuel, so the car does not emit any harmful gases into the environment.
Related Post: How To Test Intake Air Temp (IAT) Sensor With Multimeter
How Does Intake Air Temperature Sensor Work
The intake air temperature sensor of the car is a thermistor. A thermistor is an electrical resistor that changes its resistance value with the temperature change.
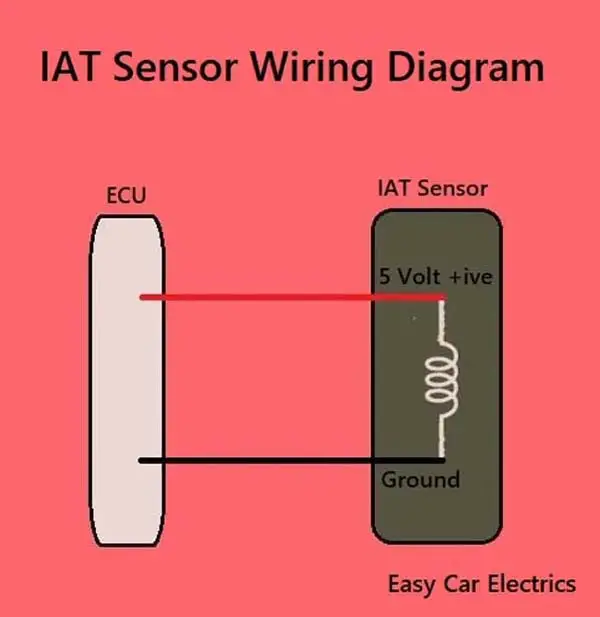
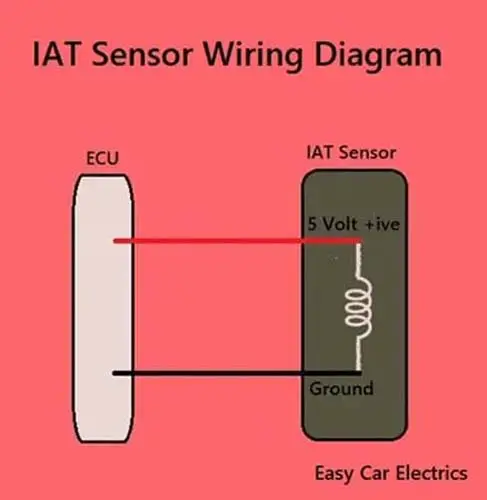
A 5-volt is applied to this temperature sensor known as the reference voltage by the ECU of the car, and it monitors the voltage that comes back to it by the IAT sensor signal wire.
As a temperature sensor changes its resistance also changes according to the temperature, the temperature sensor allows the voltage back to the ECU according to the temperature. Then ECU analyzes the voltage received back to it by the temperature sensor, the voltage signal received back will tell the ECU about the current temperature of the air.
The ECU is already programmed about the intake air temperature sensor’s input and such amount of voltage received back to the ECU indicates such amount of air temperature. The ECU uses the information obtained from the IAT sensor to maintain the correct air-fuel ratios in the mixture inside the combustion chamber.
Most IAT sensors are Negative coefficient temperature (NTC) thermisters means their resistance decreases with an increase in temperature.
Hot air (high-temperature air) will decrease the resistance and send back high voltage to the ECU while cold air (low-temperature air) will increase the resistance of the sensor and send back low voltage to the ECU. (High temperatures result in high voltage values at the sensor, and low temperatures result in low voltage values).
Due to this, the ECU adjusts the amount of fuel to inject into the combustion chamber to improve the fuel economy. Some intake air temperature sensors are Positive Coefficient temperature thermister means their resistance increases as the temperature increases.
Related Post: 7 Symptoms Of Bad Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
IAT Sensor Location
The IAT sensor is located in three different locations such as in the air duct of the air charge pipe, in MAP, and in MAF sensors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
IAT sensor is short for Intake Air Temperature sensor. It is used to measure the temperature of the air going into the engine. The MAF sensor is short for Mass Air Flow sensor. It is used to measure the amount of air flowing into the engine.
The IAT sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the engine. The ECU uses this information to adjust the amount of fuel injected into the engine. The colder the air, the more fuel is injected into the engine. This is because cold air is denser than warm air and therefore contains more oxygen. More oxygen in the air means that more fuel can be burned, which results in more power being produced by the engine.
Sign Up