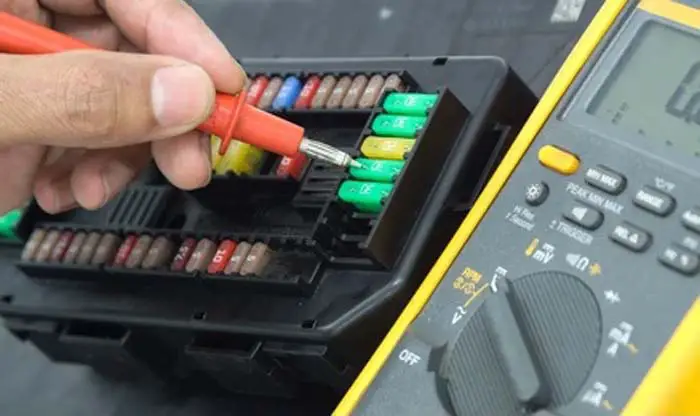
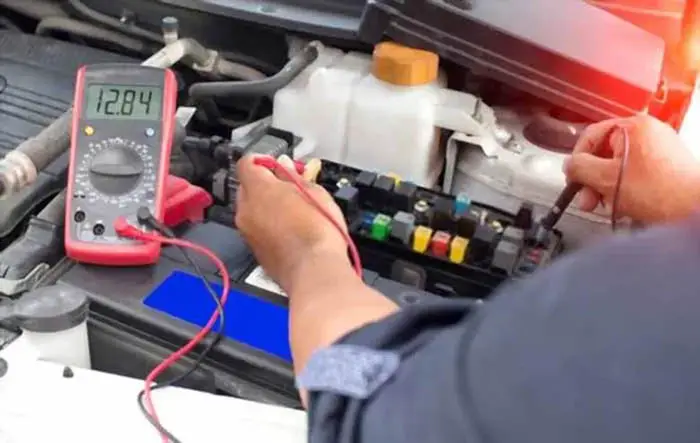
In a car, the fuse is a device that is used to protect the electrical circuits from overloads. The fuse is placed in between the battery and the electrical system and it acts as a safety switch that will cut off the flow of electric current if there is too much current flowing through the circuit.
If you’re like most people, you probably don’t know how to check a safety switch without extracting it. Don’t worry, it’s actually quite simple. All you need is a multimeter. With a DMM, you can easily check to see if a fuse is blown without having to remove it from the fusebox. Just follow these simple steps and you’ll be checking fuses like a pro in no time.
What You Need to Know Before Testing a Fuse with a Multimeter
Before testing a fuse using a multimeter, it is important to ensure that the circuit the fuse is protecting is not live or energized. This can be done by turning off the power to the circuit at the main breaker or fuse panel. It is also important to ensure that the multimeter is set to the proper setting for measuring continuity or resistance.
How To Check Fuses Without Removing Them With Multimeter
Method 1. Testing A Fuse Without Removing Them Measuring The Voltage

In this method, you will learn how to find the fuse and test them without removing the fuse.
In this testing method, volt potential is measured on every terminal side of the fuse with a DMM without pulling them out of the fusebox. If the volt potential is measured in both terminals of the fuse then the fuse is good and if the voltage is measured in one terminal of the fuse, not in another terminal then the fuse has blown and you’ll need to replace it. A further step by step guide is provided below.
Step 1. Move The Dial To DC Volt Mode
Grab the multi-meter and move the selector to 20-volt DC mode and put the black piece of wire in the common socket and the red lead in the volt potential socket.
Step 2. Turn ON The Suspected Fuse’s Circuit
Turn the meter ON of the suspected fuse’s circuit to ensure that the circuit is complete and the electrical current is flowing in the circuit. This will allow the volt potential to be measured across the fuse using a digital voltmeter.
Step 3. Check The Fuse

Place the tips of both leads on the fuse metal end caps and look at the display of the voltmeter. You will see zero or near-zero voltage, which means the fuse is good. If the volt potential across the fuse is the full supply voltage, it means the fuse is bad and needs replacement.
Method 2. Testing The Fuse With Multimeter Using Body Frame Method

You can also test the fuse the other way around by putting the black probe of the multi-meter on the battery negative terminal or body frame and the red probe on the fuse terminals one by one. Check the digital multimeter reading, if the volt potential is the full supply volt potential (reading is similar) in both terminals of the fuse this indicates a good fuse.
If the DMM reads the full supply voltage in one terminal and does not read the full supply volt potential in the second terminal, it means the fuse has blown. In this condition always replace a fuse with a new one to ensure that the flow of current is regulated.
Related Post: How To Test A Fuse With A Multimeter: 2 Simple Methods
Can You Test Car Fuses Without A Multimeter

Yes, it is possible to test automotive fuses without a DMM. One way to do this is to use a test light, which is a tool that has a small light bulb and a pointed probe. The pointed probe is inserted into the end of the fuse, and the light bulb will light up if the fuse is good. Another way to test a car fuse is to use a continuity tester, with this device you will hear a beep if there is a connection. These can be found at an auto parts store or online.
Dangers of Incorrectly Testing Fuses with a Multimeter
- Short Circuit: One of the most serious dangers of incorrectly testing fuses with a DMM is the risk of a short circuit. If the leads of the multi-meter are not properly connected, there is a risk of electrical current flowing through the multi-meter and potentially causing injury.
- Damage To The Fuse: Another danger of incorrectly testing fuses with a DMM is the risk of damaging the fuse itself. If the multi-meter is not set to the proper resistance value which is measured in ohms (Ω), or if the leads are not properly connected to the fuse terminals, it is possible to apply too much volt potential to the fuse, which can cause it to blow or become damaged.
- Damage To The Multi-meter: In addition to the risk of damage to the fuse, there is also a risk of damage to the multi-meter itself. If the multi-meter is not set to the proper resistance measurement range, or if the leads are not properly connected to the fuse terminals, the multi-meter may be damaged by electrical current flowing through it.
- Inaccurate Readings: Incorrectly testing fuses with a DMM can also lead to inaccurate readings, which can cause confusion and potentially lead to further problems. For example, if the multi-meter is not set properly it will measure the resistance value incorrectly, and the reading may not be accurate, which can lead to a false indication of whether the fuse is good or bad.
- Fire Hazard: In some cases, if the fuse is not tested correctly with a multi-meter, it may cause a fire hazard. If a fuse that is actually blown is not identified, it may allow too much current to flow through the circuit, which can cause overheating and potentially lead to a fire.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fuses are important components and sometimes these fuses require testing to check whether the fuse is in good condition or not. Under such conditions testing fuses with a DMM is a useful way to determine whether a fuse is good or bad. But, it is important to take the necessary precautions and follow proper procedures to avoid the dangers of incorrectly testing fuses with a multimeter. Always make sure to turn off the power, use the correct range, and properly connect the leads to avoid any possible hazards.
Related Post: What Is A Car Fuse, How It Works: Ultimate Guide
FAQs
To check if a fuse has blown, you can use a visual inspection (check the fuse to see its condition), a continuity test, or a quick test. A visual inspection involves looking for any physical damage or discoloration on the fuse. A continuity test involves using a DMM to check for a closed circuit on either side of the fuse. A quick test involves checking the resistance of the safety wire with a digital DMM. If the fuse has blown, it will show an open circuit by preventing current from flowing and will need to be replaced.
If your fuse is working badly you need to replace the old fuse with one which is new. The fusebox in a car is usually located in the engine compartment or under the dashboard which contains different sizes of fuses. It may also be located in the trunk or under the hood. To find the fusebox, you can refer to your car’s owner’s manual or consult a mechanic.
To replace a blown fuse, you will need to find the fusebox inside your car, locate the blown fuse, and remove it. Then, you can replace it with a new fuse of the same type and size. It is important to ensure that the new type fuse is rated for the same current as the old one, as using a fuse with a higher rating can cause an overload of current and damage to your car’s electrical system.
A slow blow-fuse is designed to allow a temporary overload of current to pass through without blowing. A fast blow/burnout fuse, on the other hand, is designed to blow quickly in the event of an overburden of current. Slow burnout fuses are typically used in applications where a temporary surge of current is expected, such as motors starting. Fast burn-out fuses are typically used in applications where an immediate interruption of the current is needed, such as in the protection of electronic devices.
You can test a car safety switch without extracting it by using a digital multimeter. Set the dial to the lowest setting on the multi-meter, then place the leads together to get an initial reading. Next, touch one lead to one end of the fuse and the other lead to the other end of the fuse. The reading should be similar to the initial reading. If the reading is not similar, it means the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced. Place the fuse and look for a marking on the fuse to identify its type.
When replacing a fuse on a non-conducting wire, it is important to use a safety wire that is rated for the same current as the original fuse. The fuse wire should be inserted on one side of the fuse and connected to the one lead of the wire. On the other side of the fuse, the wire should be connected to the positive battery terminal. This will interrupt the flow of current in the event of an overload, protecting the wire and the car’s electrical system.
There are many different kinds of fuses available, each fuse is designed for specific applications. Some common types of fuses include fast burnout fuses, slow burnout fuses, glass fuses, ceramic fuses, and blade fuses. Each kind of fuse has its own characteristics and uses according to the components inside the fuse. For example, fast burn-out fuses are typically used in the protection of electronic devices, slow burnout fuses are typically used in motor starting, glass fuses are typically used in older electrical systems, and ceramic fuses are typically used in high-volt potential applications. Blade fuses are typically used in automobiles and other small electrical systems.
Related Post: 7 Types Of Automotive Fuses: Car Fuse Types W/Pics& Charts | The Ultimate Guide
Sign Up




