Fuses are the gatekeeper of an electrical circuit. It sacrifices itself when the current flow exceeds the pre-determined rated current flow. There are various types of automobile fuses. They come in different sizes, configurations, shapes, and designs. Each fuse has its characteristics and applications.
Below is the ultimate comprehensive list of different types of car fuses. In this powerful guide, you will quickly learn about the different types of fuse your vehicle use with a complete ampere rating chart and pictures.
Different Types Of Car Fuses:
Fuses are designed to blow preventing the electrical circuit from burning. There are hundreds of vehicle fuse varieties and designs. automobile fuse types vary in terms of make and model. Each fuse has its specification, design, and installation depending upon the need of the circuit. The major types of fuses are either of these:
- Fast Blow Fuse
- Slow Blow Fuse
Fast-blow fuses are fuses that blow immediately during a short circuit while a slow-blow fuse blows after some time during a short circuit.
Types Of Fast Blow Fuse
Here are the four types of Fast-Blow Fuses
- Glass Tube Fuse
- Blade Fuse
- Bosch Fuse Or Torpedos Fuse
- Electric Vehicle Fuse (EV Fuse)
1. Glass Tube Type:

Automotive glass tube type fuse is the primary fuse used in the initial era of the vehicle before blade-type fuses were invented. Glass fuses consist of two metal end caps terminals with metal wire. This metal wire is internally connected with the end caps terminal to provide a path for electrical current.
Glass tube fuses were constructed to fail in the event of overcurrent. It burns itself due to a fault in the circuit. All the glass tubes are almost ¼ inch wide in diameter with different length sizes depending on the amperage rating.
Glass tube fuses are fast-blow fuses and burn immediately in overcurrent events. It was first used in the 1910s in fuse holders, nowadays these fuses are rarely used in cars. It comes with a current of 4 amp to 30 amp.
2. Car Blade Fuse:
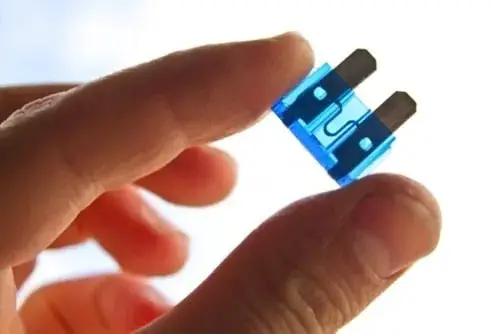
Blade-type fuses are also known as Plug-in fuses, developed first in the 1970s. It is the most common automotive fuse type used in the car industry. A blade fuse is a type of automobile fuse consisting of two blades/prongs and a fuse-element (A metal wire connecting both blades) encased in a semi-transparent color-coded plastic. The purpose of a transparent plastic housing is for easy identification of a broken fuse.
The main job of the fuse is to protect the wiring from catching fire. The fuse element is within the fuse which is one of the most important components within the car. When excessive current runs through the fuse, its metal wire temperature increases and the fuse element melts which causes the breaking of the circuit. The metal wire present between the two blades has a lower melting point compared to the entire electrical path. Blade-type fuses are easy to remove and replace. This feature gives it an edge over other fuses.
This is an Info
The purpose of the fuse is to protect the wiring harness and electrical components of the vehicle from damage. The fuses feature an internal fuse element that melts, when a high amount of current passes through the fuse element, causing the breaking of the circuit.

The fuse size varies depending on the amperage rating. The higher the amperage rating the more width it has. The blade-type fuse has its own color-coding system to represent a specific amperage rating which indicates how much current a fuse can handle. The fuses designed for automotive come in different sizes with the current rating. there are commonly six different sizes with current ratings according to their width.

Fuse type and amperage are the two most important factors. Fuse amperage rating represents an amperage rating in two different ways. First, through color coding. The housing body of each blade-fuses is color-coded with a specific color associated with a specific amperage rating, hence the color of the fuse tells you about its amperage rating. The second method of showing the current rating is the amperage rating printed on the plastic housing body of the fuse.
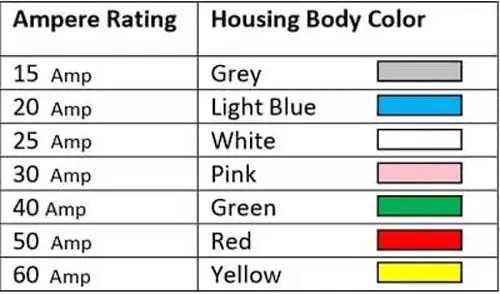
One informational point you need to know is that all types of blade fuse do not start from the same amperage rating. Maxi-blade fuse starts from 15 amp and continues to 120 amp. Whereas micro-blade fuses are available in the range of 5 amp to 30 amp. Similarly, regular blade-type fuses are in the range of 1 amp to 40 amp. Hence different diameter sizes when compared tells the comparative amperage.
Also, bear in mind that the plastic housing body of a fuse can repeat and makes you confused. In a regular blade type fuse, the 10 amp fuse color is red. The same Red color in the maxi-blade fuse represents 50 amp. These are the cautions, one must keep in mind while replacing fuses, especially in worry situations. There are various dimensions, colors, and types of fuses that come in to represent its characteristics.
Related Post: A Car Fuse Guide
Types Of Blade Fuse:

Types Of Blade Fuse
- Blade fuse has four main types.
- Regular Fuse: ATO & ATC Fuses:
- Mini Fuse: APM/ATM
- Micro
- Maxi-Blade Fuse (APX):
1. Regular Fuse: ATO/ATC:

A regular fuse is the standard type of blade-fuse first introduced in the late 1970s. Vehicles using a blade fuse type are the most common fuse type. These fuses are predominantly used in automotive and marine applications. It is the second-largest type of blade-fuse in size. You can recognize it by its wider width than its taller height. Standard type fuse comes in two main varieties called ATO & ATC fuse. They both are the same in size and shape and are also interchangeable with each other provided that the amperage rating is the same.
What Are ATO And ATC Fuses:
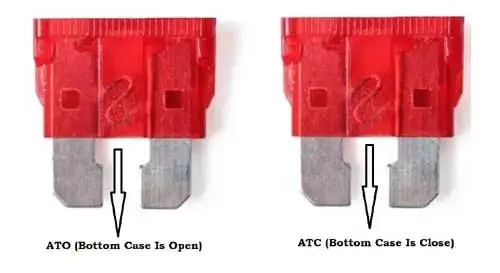
First let me make it clear that ATO/ATC only relates to the design of the housing body of the fuse, not to anything else. Car manufacturers made plastic housing bodies of a fuse in two different designs.
In the first design, the bottom of the plastic housing body of a fuse is kept open, exposing the fuse-element to the atmosphere, called the ATO fuse. Where the “O” at ATO stands for “Open” housing space between the two blades of the fuse.
In the second design, the bottom of the plastic housing body is kept closed, sealing the fuse-element from the atmosphere (To protect the fuse-element from moisture), called the ATC fuse. Where “C” stands for “Closed” housing space between the two blades of the fuse.
Important Note:
In the automotive industry, it doesn’t matter whether you use ATC or ATO fuse. This care is only kept in an explosive environment, especially in marine applications. Where the fuse does not burn the gas fumes like in the boat bilge area. Regular fuse comes in a variety of different amperage ratings from 1 amp to 40 amp. Below is the Ampere Rating chart of Regular Fuse.

2. Mini Fuse: APM/ATM:

Also called APM or ATM fuse where “M” denotes Mini. Mini-type fuses are smaller in size than standard ATO/ATC fuses. With advancements in technology, the circuit demands of a car increased. Therefore, the need for more electrical paths to be controlled in a limited space evolved. For this reason, the mini-type fuse was introduced.
It was first developed in the 1990s. It can control more circuits by occupying less space. Mini-type fuses have the same characteristics as regular fuses. It is available in a variety of different amperage ratings from 2 amp to 40 amp.
Mini-type fuses have the same amperage color coding as regular fuses. These safety switches are also available in a smaller version called low profile mini fuse. Here is the Ampere Rating chart of the Mini-type Fuse.

A. Low-Profile Mini Blade Fuse: (ATM/LP):

Low profile mini blade-fuse is the type of mini fuse and has the same characteristics as regular mini fuses contain. Also, it has the same body housing height and width as regular mini fuses have. But the only difference is that the blade terminal of the low profile mini fuse does not exceed the bottom of the plastic housing body, which allows an Ultra-low fuse to save more space and weight.
It saves additional space and weight due to its overall small height. Ultra-low Fuse has the same color coding as a regular mini-type fuse contains. It comes in an amperage rating of 2 amp to 40 amp. Here is the Ultra-Low Fuse Amp rating chart.

This is an Info
Low-profile mini-blade-fuses have the same body housing height and width as regular mini-fuses. But the difference is that the blade terminal of the Ultra-low mini fuse does not exceed the bottom of the plastic housing body.
3. Micro:
Micro fuses are the smallest type of automotive blade fuse. It became the new standard for automotive vehicles. Micro fuses are great for high-temperature environments. It comes in two types.
- A. Micro 2 (Also called two-prong blade-fuse)
- B. Micro 3 (Also called three-prong blade-fuse)
A. Micro 2:
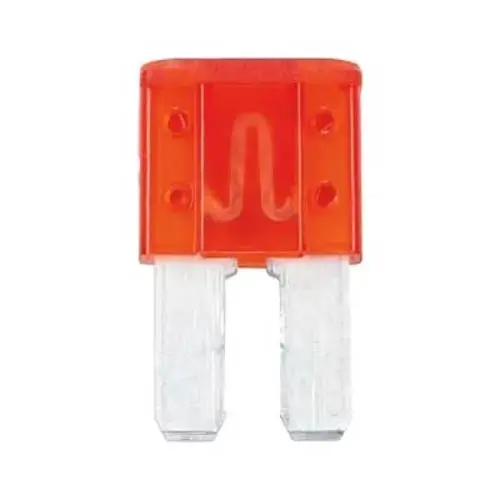

Also known as APT, ATR, or 2 Prong. Micro 2 is the smallest type, surpassed the mini fuse, and became the new standard in vehicles. Generally, people get confused between mini and Micro 2 fuses. You can identify the Micro 2 fuse easily by its height. Micro 2 fuse is much taller than wider in size. Conversely, the mini-type fuse is a little wider compared to the micro 2 Fuse.
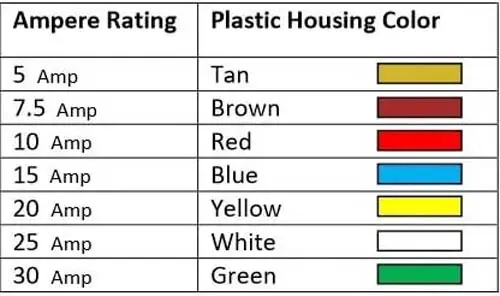
Its design and structure can save more space and control more electrical routes. Its amperage rating range is from 5amp to 30amp. Below is the amp rating chart of the Micro 2 fuse.
B. Micro 3:
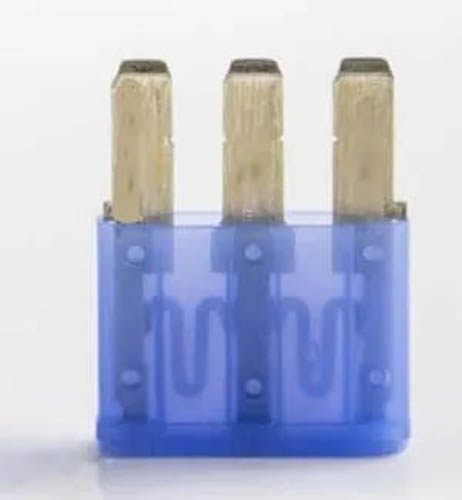

Also called ATL or 3 Prong. Micro 3 is a three-Prong fuse. It has a middle common terminal that provides current to either side of the terminal through a fuse-element. You can say, overall it has three terminals and two fuse-element wires with a central common terminal.
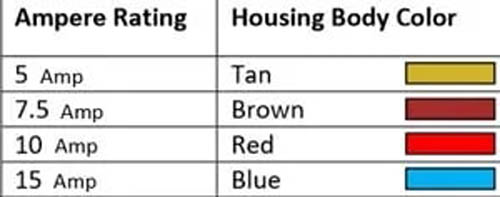
This allows a single fuse to effectively control two electrical paths. Also, its small layout can control more electrical paths while using less space. Its amperage rating varies from 5 amp to 15 amp. Below is the amp rating chart of the Micro 3 fuse.
4. Maxi Blade Fuse (APX):

Maxi fuse is the largest in size. These fuses are found in older vehicles with high amperage electrical routes. It is used in heavy-duty applications, especially for motor-powered applications where a large inrush current is needed at the start.
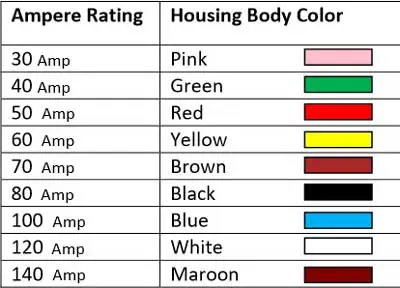
In the past, it was mainly used in place of fusible links. It is available in different current ratings from 15 amp to 120 amp. Here is the amp rating chart of the Maxi-Blade Fuse.

3. Bosch Fuse Or Torpedos Fuse (ATS Or GBS):

Bosch fuses are common in cars. Bosch-type fuses roughly look like glass-type fuses in shape. It is made up of plastic material and has two conical end caps which are pointed outside. Due to these conical end caps, it is also called Torpedos Fuse.
Bosch-type fuses are also containing a thin metal strip that connects two end metal caps with each other. This conductive strip wire is designed to fail when the overcurrent event happens. These fuses are replaced by blade fuses.
4. EV Fuse:

Electric vehicles (EV) fuse is a high-voltage, high-current rating fuse. It is used in high-voltage batteries or hybrid electric vehicles for protection from overcurrents.
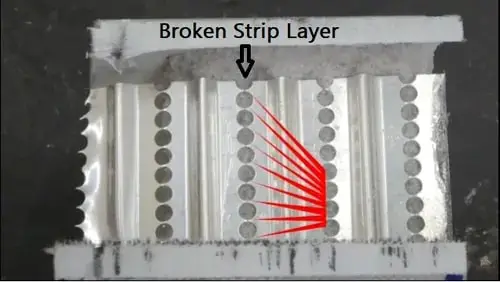
EV fuse consists of layers of strips that carry the current. It is sealed with silica sands or some other powder so that when the fuse blows, it leads the arc to disappear. The fuse has the characteristics of fast-acting whenever a short circuit occurs. It is available in voltage ratings up to 1000 V DC with a current rating of up to 1000 Amp.
Slow Blow Fuses:
A slow-blow fuse is a fuse that can withstand an excessive amount of current for short time without blowing itself. It is used in applications where the harmless high inrush current is needed for short time during a start-up like a starter, alternator, etc.
Some car applications by nature need a large inrush current at a start-up that exceeds a fuse’s pre-determined rated current value. If a fast-blown safety switch is used, it could blow immediately resulting in the wrong nuisance blowing.
By using a slow-blow fuse you can bypass this false tripping problem. A slow-blow fuse fulfills the overload demand of applications without bursting itself. It bursts only when the overcurrent situation sustains an electrical path.
It has the characteristics of built-in time delay and low voltage drop. Its fuse-element material is designed to slowly raise its temperature when the current overruns the electrical path, which protects the fuse from false blowing. Thus, a slow-blow fuse melts after some time in an overload event.
Types Of Slow Blow Fuse:
Here are the three types of Slow-Blow Fuses.
- Bolt Down Fuse:
- Fusible Links:
- Cartridge-Fuses:
5. Bolt Down Fuses
A bolt-down fuse is used when more power is required and limited space is available. Bolt-down fuses meet all the requirements and features of high-power wires. Its tin-plated contact saves space and protects the fuse from moisture corrosion.
Bolt-down fuses have the characteristics of time delay. When a high amount of current flows through these fuses, its temperature raises slowly and doesn’t blow immediately. It comes in an amperage rating of up to 500 amps. Bolt-down fuses have two types.
- A. Midi Fuse: (ANL)
- B. Mega Fuse
A. Midi Fuse: (ANL)

Midi fuse is best for space-saving of high current wiring protection. This kind of fuse is generally used for protecting the main power source wires. It is a slow-blow fuse and has the characteristics of time delay. These automobile fuses are designed so they don’t blow suddenly.
Its fuse-element heats up slowly when exposed to a high current and does not burst immediately. It is available in different amperage ratings from 30 amp to 200 amp. Below is the chart of the Midi Fuse amp rating.

Related Post: O2 Sensor Heater Fuse Location
B. Mega Fuse:

Mega fuse is a new standard for high-current wires. It is used for high-current vehicle applications, especially for battery and alternator protection. Its thin tin-plated contact, which saves space, is the reason it is an excellent choice for high-current wires.
It also has the characteristic of time delay. It comes with an amperage rating of 80 amps up to 500 amps. Here is the amp rating chart of the Mega-fuse.

6. Fusible Links:

Fusible links look much different than the normal fuse. It is a low voltage of a short piece of smaller diameter cable. It is designed to melt when the current passes its pre-determined current values.
The fusible link is the weakest wire and handles less current compared to the entire electrical route. It is about four wire sizes (AWG) smaller than the circuit wire. Its insulation is made up of special non-flammable material so that when the wire melts it remains intact. Many car manufacturers have replaced fusible links with PAL fuses.
7. Cartridge Fuses:
This is another type of slow-blow rectangular fuse used mostly in Japanese cars. It is used especially for high-current applications in which it can withstand high temperatures for a long time. These fuses have built-in extended time delay and voltage drop features.
The top window of the cartridge-style fuses is transparent for quick identification of broken fuses. It comes both in male and female terminals. The male terminal of cartridge-style fuses has either a bent or straight leg that can be bolted down.
Related Post: How To Check Fuses Without Removing Them
Types Of Cartridge Fuse:
Here are the four types of cartridge-style fuses.
- J-Case Fuse:
- Low-Profile J-Case Fuse:
- M-Case Fuse:
- PAL Fuses:
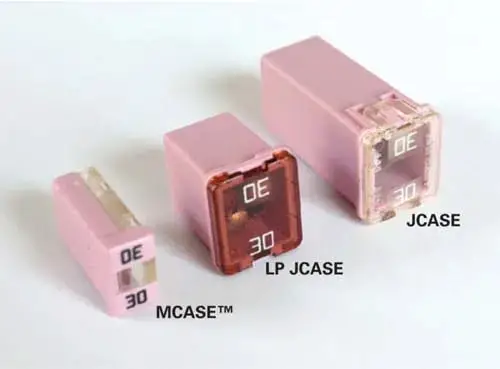
1. J-Case Fuse:

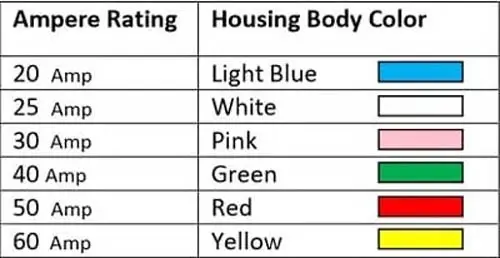
J-Case is a type of cartridge-style fuse with a female terminal design. It has the nature of built-in time delay and low voltage drop feature.
Moreover, it can handle high inrush currents. It is also called the female version of the blade-type fuse and is available from 20 amp to 60 amp. Here is the chart of the J-Case fuse amp rating.
2. Low-Profile J-Case Fuse:

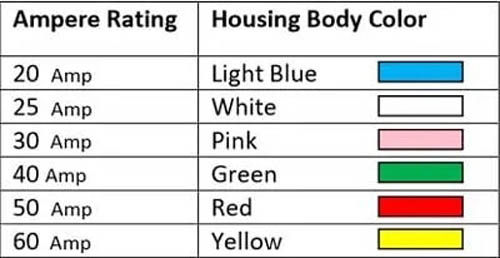
It is the mini version of the standard J-Case fuse and has similar performance characteristics to the standard J-Case fuse. Its smaller height saves more space and weight.
One plus point of a short male blade terminal is it saves more weight and material in the fusebox. It is available with a current rating of 20 amp to 60 amp. Below is the current rating chart of the Low-Profile J-Case Fuse.
3. M-Case Fuse:
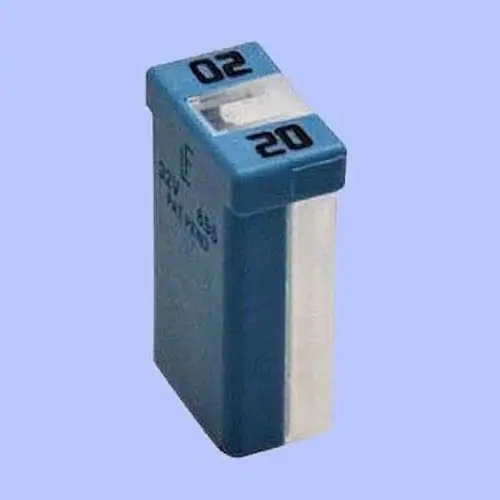

M-case is a cartridge-style fuse with female terminals. It has time delay and voltage drop characteristics. M-case is specially designed for high inrush currents applications. It comes with a current rating of 15 to 60 amps. Here is the chart of the M-Case fuse amp rating.
4. PAL Fuses:
PAL fuses are cartridge-style fuses that come in long and short legs. Some of the PAL fuses have female terminals while others have straight and bent bolt-on-legged terminals.
One major benefit of the female terminal PAL fuse is that there is no longer a problem of losing the tension of the female terminal in the fuse panel from repeated removal and insertion. PAL-fuses are mostly found in Japanese cars. It is available in the current rating up to 140 Amps. Below is the amp rating chart of the PAL fuse.
Find Your Car Fuse Box – Here’s How
Locating a vehicle’s fuse box can be done using the owner’s manual. It is typically found under the steering wheel or in the engine, but it may be located in other areas depending on the model. It is best to look for the fusebox in a well-lit location on a flat surface. If the owner’s manual does not provide the location, it can be found online. Locate the fuse box and identify the kind of fuse using the owner’s manual or fuse box diagram.
Once the fuse-box is located, it is important to use caution when accessing it and replacing any necessary fuses. Another thing you must be cautious of is identifying the fuse type. Once you identify the kind of fuse you need, you can replace it easily. Some vehicles have one fuse box while others have two fuse boxes or more than two. These fuseboxes reside inside the fuse block of the vehicle.
How to Identify The Type of Fuse For Your Car: Blade fuse Type
Identifying your vehicle’s particular fuse type, especially a blade-fuse type can be done in two ways. The easiest way to identify the specific fuse is to inspect the fuse itself, where the amperage rating is typically noted on or near the top of the fuse. The second is to check the fuse diagram in the vehicle, to understand which fuse kind is in each slot. Blade fuses are the largest automotive fuses. It has been an industry standard since 1981 and comes in different types.
The most common blade-fuse type is the flat shape, which features two prongs, or blades, on one side which easily plug into the fusebox. Other blade-type fuses may include MICRO2, MICRO3, and LP MINI. Knowing the type of fuse your car uses is important when hardwiring a dash cam or any other electronic device.
What type of Automotive Fuse Do I Need
When it comes to automotive fuses, there are a variety of types of automobile fuses and sizes needed to protect the electrical system of a vehicle. automobile fuses help to prevent short circuits, which can cause too much current to flow, potentially leading to electrical fires. To provide the best protection, it is important to choose the right fuse that is suitable for the power of the needed project.
For instance, a 300-watt amplifier will need a 30A fuse if it is a class D or 40A if it is a class AB. Furthermore, it is also wise to buy a selection of fuses and have some spare, as these are essential for preventing damage to the car’s electrical system.
Does a Blown Fuse Mean I Have a Problem in My Car
A broken fuse in a car can indicate a major problem. When a fuse has blown, it shows some symptoms which indicate an issue with a fuse including a loss of power to one or more of the vehicle’s functions or accessories, such as windshield wipers, power windows, or radio. The surest sign of a broken fuse is if the car’s electrical system stops working as the fuse box controls the electrical system of the vehicle.
A broken fuse is usually caused by a current overload, or a short circuit, and can be identified by the wire element within having melted or burned from the higher electrical current. It is also possible for fuses to blow if the wrong type is inserted into the fusebox. While a broken fuse usually only causes minor issues like backup lights or interior lights not working, it can also be a sign of a more serious problem.
A damaging fuse replacement with a new fuse is an integral part of maintaining the overall functionality of an electrical system. To replace the fuse, the power to the appliance should be disconnected.
Once you disconnect the power, the replacement of the broken fuse with a new one can be done in the following manner. The first step to replace a faulty fuse is to find the fuse box, once you locate your fuse box, remove one fuse from the fusebox. There could be multiple fuse boxes and more than one fuse resides within the fuse-box, hence you must locate the broken fuse. Usually, one of the fuses gets blown. Pick that fuse from the fuse-box and replace it with a new one and you would be good to go.
FAQs
A blown fuse may result due to a short circuit. It is a safety device that protects devices such as cars, appliances, and lights from the current overload. When a short occurs, the current passing through the fuse flows too quickly and causes it to trip, blowing the fuse. This prevents harmful electricity from flowing through the device and potentially causing damage.
Knowing which fuse is in your car is important for electrical maintenance. To locate the fusebox, look in the driver’s side footwell underneath the dashboard. You may also find a second fusebox under the hood. Consult your owner’s manual for the exact location of each. Inside the fusebox, you can find a diagram that shows the position and name of each fuse. You can also check fuses by turning the car off and finding the fuse that corresponds to the malfunctioning system. If it is a blade-type fuse, you will be able to see a metal wire inside. If the wire is intact, then the fuse is good
The two main types of automobile fuses are blade-fuse and ceramic fuses. Blade-fuse is the most common kind of fuse found in modern vehicles and comes in six varieties (Micro2, Micro3, LP-mini, Mini, Standard, and Maxi), these are current limiting fuses. Ceramic fuses are designed with canonical ends and usually feature the inscription “LUCAS” fuse on them. They are rated for electrical paths no higher than 30 amps and are mostly used in older vehicles, these are also called Lucas type fuses.
Fuses are typically current-sensitive devices. Automotive fuses are used to protect the wiring and electrical equipment of vehicles. There are several different types of automobile fuses, such as blade-fuse, mini-fuse, standard fuse, maxi fuse, and glass tubes, etc which are each designed to meet specific applications, voltage, and current demands. The kind of fuse needed depends on the type of vehicle and the electrical system being used.
Sign Up




