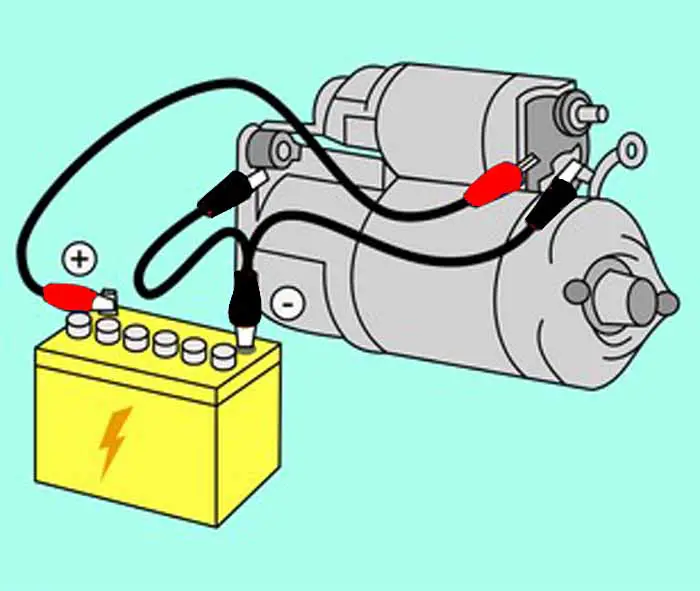
The starter motor is a small but powerful electric motor used to convert electrical energy into mechanical (rotational) energy in an IC engine to start the engine. Getting started in the car is a complex procedure. The vehicle starter is designed to work in a precise way to start the car. However, starting the car involves many more systems than the starting system.
In my last article, I explained the 11 complete and detailed car starter motor parts and functions, and now on this page, you will learn the motor process operation in deep detail. This article is going to explain comprehensively and detailed way on how a car starter motor works in easy-to-understand language.
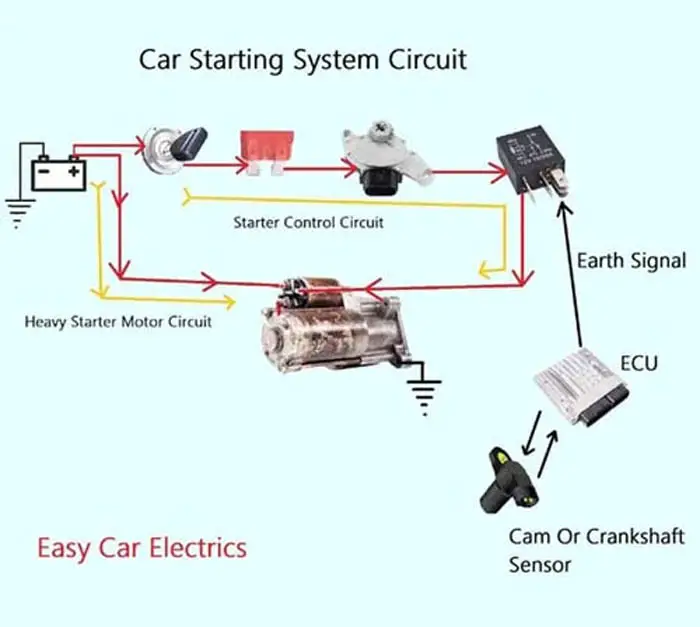
Related Post: Car Starting System, Diagram, Working, Components, Functions
What is a Starter
A starter or self-starter is a device that helps start an engine. It’s like the ignition key for your car – without it, the car engine won’t start. The starter works by using an electric motor to turn over the engine flywheel, then the engine starts running. Think of it like a bicycle – the pedals are the starter, and they help get the bike moving.
The Starter motor is located on the engine’s flywheel housing, and the car battery and the ignition switch are attached to the starter motor. When you turn the ignition switch to ignite the engine, the ignition switch sends an electric current to the motor, which then cranks the engine until it starts running on its own.
How A Starter Motor Works

The car’s starting system works by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to make the engine run.
A starter motor and solenoid are tightly integrated pairs and the heart of the starting system. It is used to turn on the engine, without it, the engine isn’t turning over and the car won’t start. To get the engine going on, it must be cranked at some speed to complete the combustion engine cycle and get the engine working.
As you know that the flywheel is very hard to rotate. The high inertia of the heavy crankshaft assembly prevents the flywheel from turning. That is why the self-starter motor requires a very high amount of electric current. A thick cable from the 12 volts of DC battery power is used to power the starter motor.
The starter motor is earthed via the case itself. The negative side of the motor is connected to the metal case of the motor which is mounted to the engine via bolts. As a result, the engine is indirectly connected from the negative battery terminals to the starter body through the chassis.
Initially, a starter motor is powered to crank the engine up to a speed sufficient to run smoothly on minimum RPM. And the motor is only used to ignite the engine as soon as the engine has started and runs on its own power, then it is not needed and burdened until the next start.

When you press the start button, the current flows to the “S” terminal of the solenoid, which is usually a pin-type or a small stud-type terminal fitted on the back of the solenoid cap. Also the “S” terminal of the solenoid consists of two types of windings pull-in and hold-in windings.
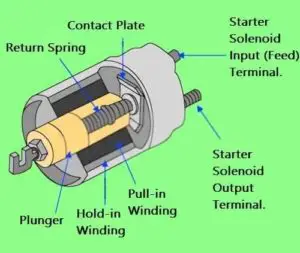
When these windings are energized, they create a magnetic field. This electromagnetism attracts the rod called a plunger inside the solenoid. This does two functions simultaneously. One is, it moves the starter pinion gear towards the flywheel by lever-fork, which is attached to the end of the plunger.
The second function is, it closes two heavy contacts that are placed at the other end of the solenoid plunger. Now here is the interesting part.
The pinion gear meshing with the engine flywheel occurs just before the starter motor run. This is done to prevent any damage to the teeth of either the pinion gear or flywheel. These kinds of starter motors are called Pre-Engaged Starter Motors. In a pre-engaged motor, the full power is not applied until the pinion gear fully meshes with the flywheel ring gear.
This pre-engage feature comes in both types of Gear Reduction and Direct Drive starter motors. I know that’s a lot to take in but bear with me, I will cover a lot more interesting points.
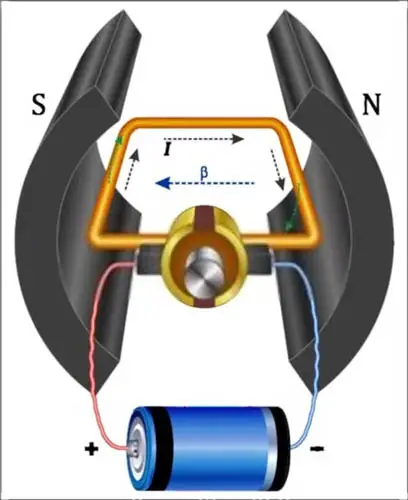
As the motor is fed with current by the solenoid, the current flows in the direction of the brushes to the commutator and then to the armature winding. The armature is fitted in the center of the starter motor (Here a coil is shown in the above picture, as you know armature is an electromagnet collection of several coils of wire). By flowing current in the armature windings, electromagnetism is produced. Electromagnetism means North and South poles.
This N-pole and S-pole react with the already available North and South poles of the electromagnet or field coil. As you know like polarities repel and opposite polarities attract each other. When the like polarities of armature and field coil or permanent magnet face each other, it repels, and the opposite polarities attract each other.
The reaction between the North and South Poles of both components causes the rotation of the armature. This rotation is then transferred to the engine flywheel by the armature shaft.
A planetary gear set or gear reduction assembly is installed on the armature shaft to increase the torque of the motor. The planetary gear set reduces the output speed of the pinion gear with a 4:1 ratio, which means with each rotation of the pinion gear, the armature rotates four times.
As the axle of the armature turns, the pinion gear also turns the flywheel, this makes the engine suck in air and fuel in the cylinder. Meanwhile, the ignition system is activated, and the current is sent to the spark plug wires to ignite the fuel in the cylinder. As a result, the car starts over. However, if the engine turns over and the pinion gear mistakenly remains intact with the flywheel,
So, it is possible the flywheel would spin the starter motor too fast which can cause damage to the motor. For this reason, an overrunning clutch is designed to slip the pinion gear from excessive turning. The overrunning clutch is located on the armature shaft just before the pinion gear. It allows the pinion gear to be spun freely when the flywheel runs faster than the pinion gear.
In the end, when the internal combustion engine starts over, the driver releases the key switch, which de-energizes the starter solenoid. The return spring inside the solenoid moves back the plunger to its normal rest position, which disengages the pinion gear from the flywheel and also, discontinues the battery current from the motor.
These are the operations that occur in a starter motor when you turn the key switch. Hope you got everything.
Types Of Starter Motor
There are two most common types of electric starter motors, namely the Direct Drive Electric Starter Motor and the Gear Reduction Type Starter Motor. These two types are further divided into different variations such as Permanent Magnet Direct Drive Starter Motor, Permanent Magnet Gear Reduction Starter Motor, Field Coil Direct Drive Starter Motor, and Field Coil Gear Reduction Motor, each with its own specific construction and design variations.
The direct drive starter motor is a conventional category of motor that is heavier and bigger in size. Due to this reason, it requires high-current battery cables and other accessories to carry the current. In contrast, a starter gear reduction starter motor is more efficient consumes less power and produces more torque.
Related Post: Types Of Starter Motor
Maintenance And Care Tips
- Keep The Starter Clean: Dirt, debris, and oil can accumulate on the starter, which can cause it to malfunction. Use a clean, dry cloth to wipe the starter down regularly.
- Inspect The Starter Regularly: Check the starter for any signs of wear and tear, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose connections. If you notice any problem with the starter, then replace a starter motor as soon as possible.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Over time, the moving parts of the starter can become dry and worn. To prevent this, lubricate the moving parts regularly with light machine oil.
- Check The Battery: The battery is a crucial component of the starter system. Make sure the battery is in good condition, fully charged, and the cables are clean and tight.
- Test The Starter Periodically: Check the starter’s performance periodically by running a starter current draw test. This will help you detect any potential issues before they become major problems.
- Keep The Starter Cool: Heat can cause damage to the starter’s components. To prevent overheating, make sure the starter is well-ventilated and not located near any sources of excessive heat.
- Avoid Overloading The Starter: Don’t try to start an engine that is too large for the starter to handle. Overloading the starter can cause it to overheat and fail.
By following these maintenance and care tips, you can help ensure that your starter lasts as long as possible and operates efficiently.
Conclusion
To sum up, a starter motor is a device that helps start an engine by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works by using an electric motor to turn the engine’s flywheel, which then starts the engine running. When you turn the key to ignite the engine, the starter switch sends an electric current to the motor, which then cranks the engine until it starts running on its own. The starter motor requires a very high amount of electric current to rotate the hard flywheel. The typical starter solenoid is an integral part of the starter, and it works by creating an electromagnetic field that attracts the plunger and moves the pinion gear toward the flywheel. The rotation of the armature is then transferred to the engine flywheel by the armature shaft, which increases the torque of the motor.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
If an engine starter is wired incorrectly, it can cause a number of problems in the starter circuit. The most common problem is that the engine will not start. The current will not flow through the starter correctly and the engine will not start. This is because the starter needs a certain amount of current to flow through it in order to work properly. If the current is not flowing through the starter correctly, then the engine will not start. In some cases, a short circuit can occur and the starter can overheat and gets damaged.
There are a few different types of vehicle starters, so the number of wires will depend on the specific starter. Generally speaking, however, most vehicle starters will have at least three wires. Two of these wires will be connected from the solenoid to the battery, and the other one will be connected from the solenoid inside the self-starter motor.
A self-starter motor is a component that turns the engine of a car, allowing it to start. It is typically activated by turning the ignition key switch and begin the combustion process, which engages the starter control circuit and the starter relay, causing the starter motor to spin the engine.
The main components of a starter motor include the starter motor housing, starter relay, starter motor gear, soft iron core, two coils of wire, and four fields. When the ignition key switch is turned, the starter control circuit activates the starter relay, which connects the starter motor to the battery. The soft iron core is made of a laminated soft iron core, wrapped in two coils of wire, and contains teeth on the starter that mesh with the starter gear. When the starter motor turns, it pushes the starter gear forward to mesh with the teeth on the flywheel or flexplate and then turns the engine over, allowing the combustion process to begin.
Some common signs of a bad starter include a clicking or grinding noise when trying to start the car, the engine failing to turn over, etc. A defective motor can be caused by a number of factors, including a worn-out starter relay, a broken or worn starter gear, a damaged laminated soft iron core, or a faulty connection between the starter and the battery.
If your car’s starter motor is faulty, the starter may need to replace it. To do this, you’ll need to disconnect the battery, remove the starter from the car (which may involve removing other components to access it), and then replace it with a new one. If you’re not comfortable doing this yourself, the car might need to be taken to a professional mechanic or car repair shop. Before replacing the starter, it’s also a good idea to check other components, such as the starter relay and starter gear, to ensure that they’re not the source of the problem.
Sign Up