Do you know what a fuse is?
To make it simple, a fuse is a self-killer that saves the rest of the electrical circuit from overcurrent. It protects the whole circuit from catching fire.
From my experience, people don’t know why a car’s electrical fuses are very important in an electrical circuit, why we need them, and why it is very important to put the fuse in the positive wire.
All the answers and many more things you NEED to know about an automotive fuse are deeply explained in this comprehensive guide.
On this page, you are going to learn what a fuse is in a car, how it works, the components inside the fuse, the inline type of fuse, etc. And at the end of this page, you will find some important FAQs.
I can humbly say that this is the most comprehensive guide that explains the car fuse guide in easy words backed by science so that everyone can understand.
The automotive fuse market is growing rapidly due to the highest usage and demand and also giving safety to the vehicle. Its sale increased from 14.30 Billion USD in 2016 and are projected to reach 24.33 Billion USD by the year 2025.
What Is A Fuse In A Car

Fuses serve as a protection device used to protect a vehicle’s wiring harness and electrical components from damage when the current exceeds its pre-determined certain amperage values.
Fuses are typically made of a conductive metal strip (Also called a fuse element), a plastic body, and two prongs. The fuse element works as a bridge between electrical terminals and creates a path for electrical current to pass from one terminal to another terminal. Also connects two electrical terminals with each other.
The word fuse is derived from the Latin word “Fusus” which means “To Melt”. The fuse is designed to melt and break when the circuit is overloaded with the current. to prevent other electrical accessories within the vehicle
Thus a fuse kills itself in the event of a higher current. When high surges of electricity pass through the circuit’s metal strip. They play role in interrupting the circuit and halting the flow of electricity. According to fuseology by little fuse, the fuse works as a sacrificial device, which stops electric current flow to protect electrical devices and wiring harnesses from burning.
In other words, you can say a fuse controls the electrical current flow within various electrical circuits. In fact, the fuse is the weakest point of all electrical circuits. Its “Metal Strip” has a low melting point and high resistance compared to all the wiring in the circuit.
An automotive fuse is generally rated for voltages of 12 volts, 24 volts, 32 volts, and 42 volts and is rated in amperes. This ampere rating means a fuse can hold a maximum amount of current before it melts and breaks.
Fuses and relays are gathered in a fuse box under the hood of the dashboard near the driver’s side to control the electrical equipment of the vehicle. Most vehicles have two fuse boxes and the second fuse box or fuse panel is located in the engine compartment of the vehicle. Also, some components use an in-line circuit fuse, called Inline Fuse.
This is an Info
Remember, it is not the current that blows a fuse. Fuses are designed to blow due to excessive heat so it is the heat generated by the excessive current, which melts the fuse element and blows.
Related Post: How To Test Car Fuses With A Multimeter: 2 Simple Methods
Who Invented The Fuse:
It is said Thomas Edison is the inventor of the fuse.
Construction Of The Automotive Fuse:
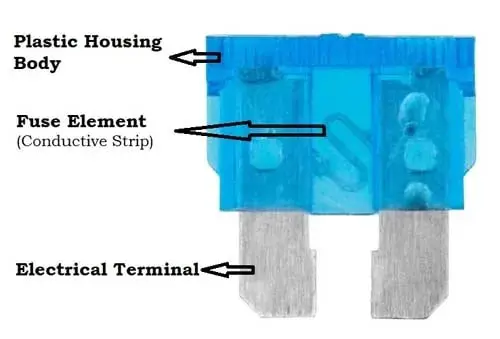
A typical fuse is a maintenance-free component and consists of a metal element with two terminals encased by the housing body of a fuse. The fuse metal element (conductive strip) is a resistive material made up of zinc, copper, aluminum, or an alloy of lead and tin, which is selected carefully for required size and amperage values.
The fuse has unique electrical and thermal characteristics and has the least deterioration due to oxidation. These metal elements are soldered to the fuse terminals inside the fuse. The metal elements have a low melting point and high resistance compared to the entire electrical circuit.
So that when the rated current is reached, it melts and disconnects the entire circuit from the power source at the correct time to prevent electrical problems.
Related Post: Construction Of Car Relay
How Do Car Fuses Work
The working principle of a fuse is based on the “Heating Effect Of Current”. The metal strip (Fuse Element) is made up of resistive material and is designed to melt and break the circuit in an overload situation.
When a high amount of current flows in a circuit, it generates excessive heat in the fuse resistive element. This is enough heat to melt and break a fuse metal element, which is called the breaking capacity. This heat causes the fuse to blow.
Breaking Capacity is the maximum amount of current at which a fuse blows safely without causing any damage to the electrical circuit. Sometimes it is also called interrupting rating.
In normal condition, the flow of current in a fuse produce normal heat in the fuse’s element (bearable heat). Which dissipates into the atmosphere and the heat level is maintained at less than the melting point of a fuse.
On the other hand, when too much current runs in an electrical circuit due to a short circuit or a wire that isn’t rated to handle such a high amount of current. This produces high temperatures in the fuse element, which is above the melting point of a fuse, causing melting and breaking down the fuse element of a fuse after which a new fuse is required to start working.
In short, a fuse protects the entire circuit from burning and works as a protective agent by disconnecting the circuit from the power source.
Related Post: 7 Types Of Automotive Fuses: Car Fuse Types W/Pics& Charts
This is an Info
When a high amount of current flows in a circuit, it generates excessive heat in the fuse resistive element, which is enough heat to melt and break a fuse metal element, which is called the breaking capacity.
What Happens When A Blown Fuse Occurs: Understanding the Mechanics of Why Fuses Blow In Every Car
When a car fuse has blown, it means that there is an electrical issue in the vehicle. The fuse is an electrical component that is designed to protect other electrical components from damage due to a power overload. Fuses come with a thin wire or filament that is placed in the circuit between the power source and the electrical component that it is protecting. When the circuit becomes overloaded, the fuse will “blow” by breaking the circuit, effectively stopping the component or system that it was protecting from functioning.
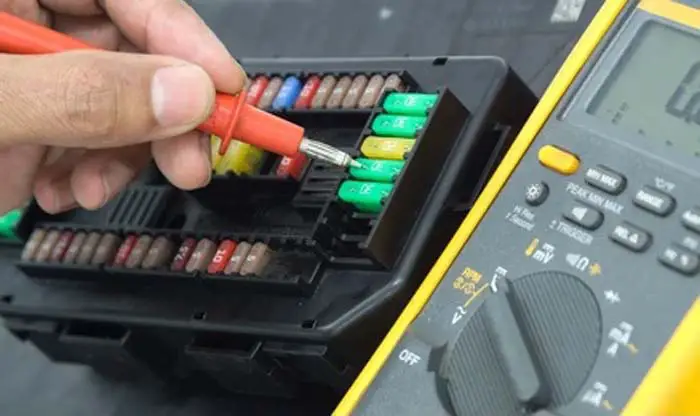
In every car, a fuse diagram is provided on the fuse box to find the fuse which helps to replace a blown fuse with a new one in the case when you suspect a blown fuse. This allows you to identify which fuse inside the fuse box you need to check if a specific component or system stops working.
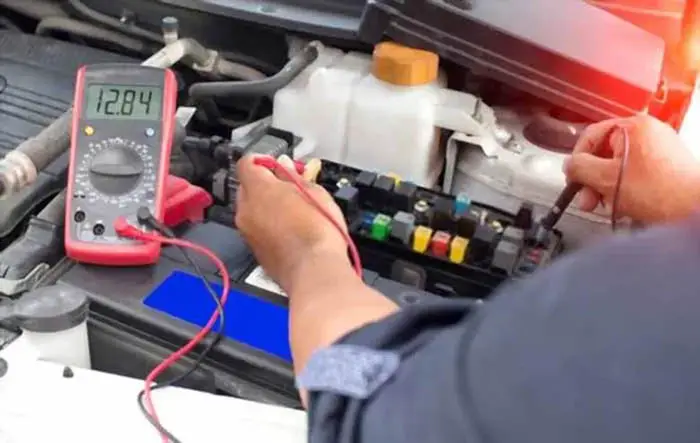
To fix the issue caused by a blown fuse, you would have to find a fuse within the fuse box to replace the blown fuse with the right fuse. You can visually inspect a blown fuse. The fuse will typically appear visibly damaged if it has blown, but if it’s unclear and it is difficult to decide anything from visual inspection, you can use a multimeter to check if it’s blown. Once you have determined that the fuse is blown, you can replace it with a new one.
It’s important to note that while a blown fuse is often the cause of a stopped-working electrical component, it is not always the case that if the fuse is blown repeatedly, your new fuse may be working properly. It’s always a good idea to check the fuse first, but if replacing the fuses doesn’t fix the problem, it’s likely that there is a more serious issue with the electrical system that should be inspected by a professional service team.
FAQs
Generally, all positive wires contain fuses in series in the fusebox to protect the circuits from harm. But, an inline fuse refers to the fuse which has a holder for the fuse fitted into the cable outside of the fusebox. So, an inline fuse is a fuse that is used in the wiring line of the circuit, not in the fusebox.
These fuses can be installed anywhere in the circuit. In general, it is best to install the inline fuse near the battery-positive power source. When fusebox space is limited or accessories that aren’t factory-installed or factory designed for circuit protection failed may have an inline fuse.
The inline fuses are most commonly used in aftermarket accessories like fog lights, aftermarket door lock unlock actuators, amplifiers, etc.
A fuse is the most common safety component. It is a basic needed device in any electrical circuit for the purpose of protection due to over current.
Whenever a short circuit happens, too much current flows through wires to generate an excessive amount of heat which is beyond the melting point of the circuit and causes fire in the entire electrical circuit.
As we know that a fuse has a low melting point compared to the whole circuit. So, a fuse is here to melt first to disconnect the circuit from the battery power source and protect the circuit from catching fire. Thus, a fuse is needed to ensure the safety of the electrical circuit.
Technically, it doesn’t matter whether the fuse goes on the positive or negative wire. You can put the fuse in either positive or negative wires. But, the best and favored location of the fuse is the positive wire of the battery power source.
If, you put the fuse on the negative wire. It only Protects the component from damage. In this case, if the fuse blows, the positive wire still has a live current.
On the other hand, if you put the fuse on the positive wire it protects both the circuit wires (Positive and Negative Wires) and as well as components. So, it is better to place the fuse on the positive wires.
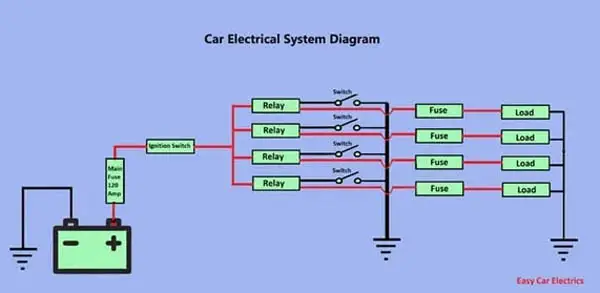
The Fuse is a kind of security guard of an electrical circuit. When there is a short or any fault that occurs in a circuit, it burns up itself rather than your wires.
You must know the best place for a fuse to perform its duty in an optimum way. The best place to put a fuse, especially an inline fuse is close to the battery. You must avoid the excessive wire distance between the fuse and the battery. If a short circuit occurs, the fuse will blow.
But, you cannot avoid the excessive wire (between fuse and battery) from melting unless a short-distance wire is used (before fusing to the battery). If for example, you put the fuse a little far from the battery, and the wire between the fuse and the battery gets shorted to the ground.
Technically, the fuse will melt and separate the remaining circuit (From the fuse to the electrical component) from the battery power source. But, the wire between the fuse and battery will melt due to a short circuit. Therefore, a fuse should be placed near the battery.
Often people get confused about which end of the fuse gets run to the battery and which end to the electrical component.
The answer is, that both ways are right. Fuses are not polarized. It does not require a specific direction for the current to flow. No matter whatever side or end of the fuse you place to the battery or component.
You can, it doesn’t harm the circuit. Fuses are direction-free safety components.
A fuse is an electrical defense component. It provides protection to the overcurrent. It does its best to protect the electrical circuits and sacrifice itself in the event of overcurrent.
When the current flows through the fuse metal element. It generates heat due to resistance, which dissipates in the atmosphere. If somehow, due to any reason, the current starts to flow high. It will generate more heat in the metal element of the fuse.
So, the metal element of the fuse will not bear such a high amount of heat. As a result, the fuse element will start to melt and blow out. This melting will discontinue the electric current flow and separate the circuit from the power source.
Thus, a fuse protects the whole circuit by melting itself.
The short answer is No.
If you replace a fuse with a piece of wire. The chances are you bypass the safety protection to over-current. A fuse works as a safeguard to an electrical circuit. It provides protection to electrical wiring harnesses and electrical components from damage.
A fuse consists of a thin metal strip, which is designed to carry a limited amount of current. If the current exceeds its pre-determined current value, the metal strip will melt and stop the flow of current. This melting in one case is a good thing. It protects the entire circuit and electrical components from catching fire.
If for example you replace a fuse with a piece of wire or rotate the wire to the blades of the fuse. There is a high chance that you will damage the protection of the circuit. This is because a piece of wire especially copper has a high melting point than the tin material used in the fuse’s metal strip.
When a high amount of current flows through copper wire. It continues to heat up the circuit but will not melt the fuse. Whereas, it will cause a fire on the wiring harness.
In conclusion, you should never go the other way replacing a fuse with a piece of wire or rotating the wire to the blades of the fuse. In one case, you can rotate the wire around the fuse is, in an emergency case.
You can use the thinnest piece of wire, according to the amp, not a thick one, until you reach the workshop. Remember, it should be a temporary solution, not a permanent one.
In one case, you can rotate the wire around the fuse is, in an emergency case. You can use the thinnest piece of wire, according to the amp, not a thick one, until you reach the workshop. Remember, it should be a temporary solution, not a permanent one.
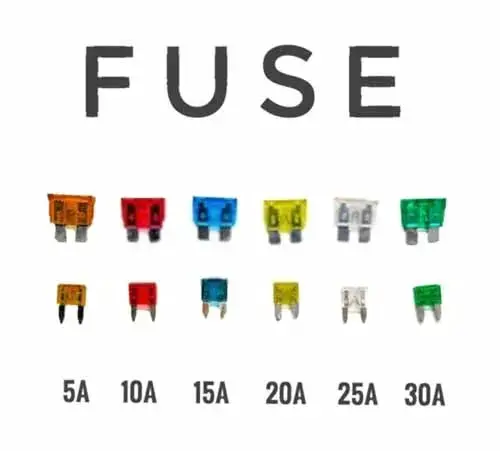

Yes, some fuses are color-coded especially blade-type fuses. They are color-coded by amperage rating. For example, a standard ATO 10 amps-rated fuses are colored Red similarly, whereas 20 amps-rated fuses are colored Yellow.
The purpose of coloring the fuse is that you don’t put an incorrect fuse in the circuit. This makes it easy to match up a replacement fuse.
The answer depends on the situation, you could and couldn’t. In general, it is unwise to use high amperage fuses instead of low amps. The current rating of a fuse indicates that the fuse will melt when the current exceeds its pre-determined rated current value for which the fuse was designed.
If an oversized fuse is used, it could cause a fire in the insulation of the wiring and also could damage the electrical components. You could use a 15 amp fuse instead of 10 amps in one situation. If you use a 10 amp slow blow fuse, you can safely use a 15 amp fast blow fuse without much worry.
To replace fuses in a modern car, you can check car owner’s manual to locate the fuse holders and use a fuse puller (most cars come with a fuse puller) to remove the old fuse and replace it with a new one.
In order to accurately accessing whether car fuses have been replaced or not, it is imperative to conduct a series of analyses. Firstly, it is necessary to inspect the physical nature of the fuse in question. If there are any visible signs of damage or degradation, then this can be indicative of a need for replacement. Additionally, it is possible to employ electrical tests such as resistance measurements and voltage drops to determine if the fuse has been compromised.
Low-profile mini fuses are small, cylindrical glass fuses that are used in some modern cars and different vehicles. They are designed to take up less space in the fuse blocks and can help you locate the fuses more easily.
Fuses are used in cars to protect electrical systems from damage by limiting the amount of electricity that can flow through a circuit. If too much electricity is flowing, the fuse will “blow” or melt, disrupting the flow of electricity and preventing damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
Sign Up




