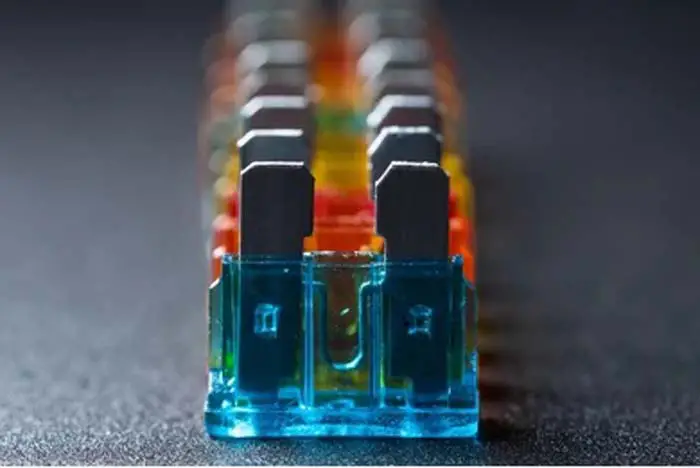
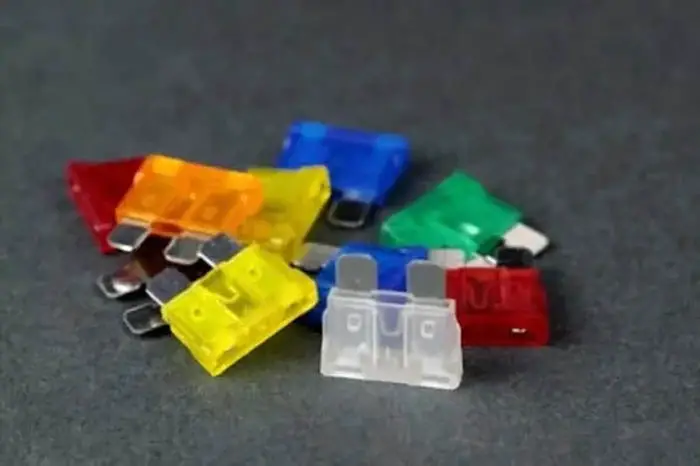
An electrical fuse is a safety device that is used to protect equipment from damage caused by over currents. A standard fuse consists of a thin conductor design that is surrounded by a cylindrical metal strip. The ends of the fuse are connected to a terminal, which is typically housed in a fuse socket or adapter. The voltage rating of the fuse is determined by the maximum current that it can safely carry, as well as its interrupting rating, which is the maximum available fault current that the fuse can interrupt.
The fuse is placed in series with the circuit and will “blow” or open if the current in the circuit gets too high. This will break the circuit and prevent excessive current flow. Fuses are made of a strip of metal that melts when too much current flows through it.
The purpose of the fuse is to provide circuit protection in your car from overheating and a fire. If there is a short circuit, the fuse will blow and interrupt the flow of current. Read more to know the purpose of the fuse and how it can protect your electrical system.
What Is The Purpose Of The Fuse:

Fuses have protected expensive equipment and prevented fires by clearing faults in electrical systems. When a fault occurs and the current exceeds the rated value of the fuse, the metal strip melts, and the fuse opens, interrupting the current flow.
This prevents damage to equipment and prevents a fire from starting. However, it is important to note that not all fuses are created equal and some fuses may have a higher interrupting rating and can handle higher fault currents. The major features of fuses are discussed below.
1. Protects The Wire From Fire
The very important purpose of the fuse is the protection of electrical equipment and wiring harnesses from damage in the event of overload or short circuits. Fuses are made of a conductive material that melts when it becomes overloaded, thus opening the circuit and preventing further flow of current.
2. Costs Low
Fuses are generally cheaper to replace when blown out. That’s because fuses are designed to fail safely by a weak point in the circuit, and they’re typically very affordable. The labor costs associated with replacing a fuse are generally lower than the labor costs associated with replacing an underlying problem.
3. Lasts Longer
A fuse body does not have any moving parts which are why it does not wear out quickly and lasts longer. As a result, it does not experience wear and tear as quickly as other devices and has a longer lifespan.
4. Needs No-Maintainance
Fuses do not need periodic cleaning or maintenance to work properly. it is important to check them regularly to ensure that they are in good working order. If a fuse is blown, it should be replaced with a new fuse immediately to prevent further damage to the electrical system.
5. Removes And Inserts Easily
The fuses are designed to allow easy replacement or change. This easy replacement makes it more useful. This makes the fuse a more versatile and useful tool, as it can be used in a variety of situations where a quick replacement is needed.
6. Good Responding Ability
With time, the fuse’s ability of protection will be the same throughout its life and will not respond poorly. This is due to the fact that fuses are designed to operate within specific parameters and do not contain any moving parts that can wear down or break over time. Therefore, it is one of the most used protective devices. As long as the fuse is used within its specified ratings, it should provide reliable protection for the duration of its life.
Related Post: How To Change A Car Fuse (7 Steps)
What is The Purpose of the Fuse Box in Circuit Protection

The purpose of the fuse box is to protect the electrical system of a vehicle by regulating the flow of electrical current. The fuse box contains fuses, which are devices that are designed to provide overcurrent protection. The fuses are wires inside the plastic housing that melt when the current flow is too high and this is to prevent a short circuit and any other electrical fault that can damage the vehicle or even cause a fire.
The fuse box is typically located under the hood or in the vehicle’s cabin, and it houses the fuses for different electrical components such as the headlights, radio, and air conditioning system. These fuses act as a safety measure to prevent damage to the vehicle’s electrical system and components by breaking the circuit if the current becomes too high. The fuse box also includes relays, which are devices that control the flow of electricity through the circuit, ensuring the safe distribution of power throughout the vehicle.
What Is The Purpose Of The Circuit Breaker In Electrical Circuit

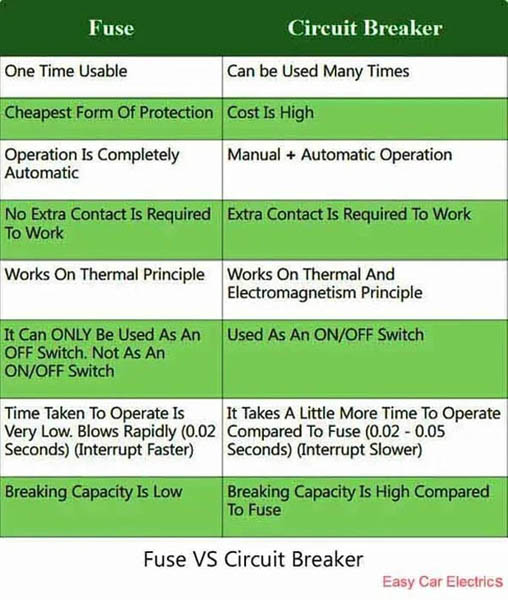
The purpose of a circuit breaker is to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overloading or short-circuiting. A circuit breaker is a current-sensitive safety component similar to a fuse that provides safety to the circuit in the event of overcurrent. The main difference between a fuse and a circuit breaker is that the fuse can be replaced after an overload event while a circuit breaker can be reset manually or automatically.
The circuit breaker uses a bi-metallic strip that is reactive to heat. The heat generated by overload in the circuit causes the bi-metallic strip to come apart and disconnect the circuit. The circuit breaker can be reset either manually or automatically. It is used in those applications where overcurrent conditions occur repeatedly.
Electrical Fuse VS Circuit Breaker
Types Of Fuse
Fuses are of different types and designs. They vary according to the make and model, but the blade-type fuse is almost standard. Each fuse has its specification and design according to the circuit demand.
There are several different types of fuses that are used in electrical systems, each with its own specific purpose. Time-delay fuses, for example, are designed to handle normal current levels for a short period of time before opening, which allows for temporary overloading of the circuit. On the other hand, a low voltage fuse is also designed for use with equipment that operates at lower voltages and has a lower current rating. Transformer fuses, as the name implies, are used to protect transformers from over currents.
Here are the two Major types of fuses.
- Fast Blow Fuse
- Slow Blow Fuse
Fast Blow Fuses:
Fast blow fuses are of four types.
- Glass Tube Fuse
- Blade Fuse
- Bosch Or Torpedos Fuse
- Electric Vehicle Fuse (EV Fuse)
Blade-type fuse is the most common type of fast blow fuse used in vehicles. The blade fuse consists of two blades soldered to the fuse element, encased in semi-transparent color-coded plastic. When high current flows, which causes the fuse element to melt and break the circuit. Blade fuse has four main types.
- Regular Fuse: ATO/ATC
- Mini Fuse: APM/ATM
- Micro
- Maxi Blade Fuse (APX)
Slow Blow Fuses:
Midi Fuse
Slow-blow fuses are fuses that can withstand an excessive amount of current for a short time, without blowing themselves. Here are the three types of Slow Blow Fuses.
- Bolt Down Fuse:
- Fusible Links:
- Cartridge Fuses:
A bolt-down fuse is used when more power and limited space are available. Bolt-down fuses have two types, Midi and Mega fuse.
Here is the most comprehensive and complete guide about different types of car fuses explained deeply with ampere rating charts.
Related Post: 7 Types Of Automotive Fuses: Car Fuse Types W/Pics& Charts | The Ultimate Guide
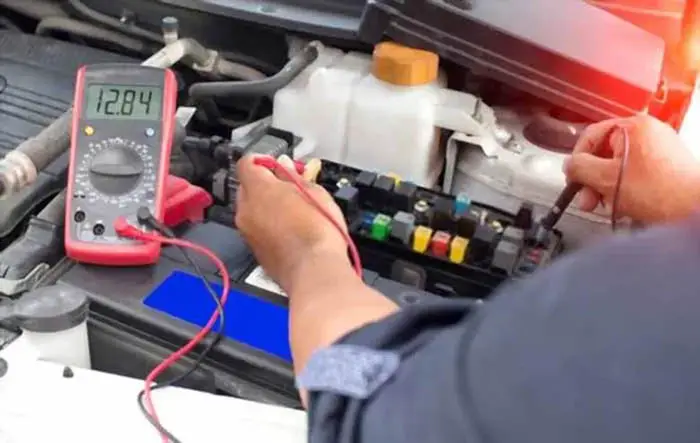
Electric Fuse Installation and Maintenance In Electrical System
Installing and maintaining fuses is relatively simple, but it is important to ensure that they are compliant with the local electrical code. When installing a fuse, it should be placed in a junction box that is intentionally placed for the protection of the equipment. The fuse should be secured in place using fuse clips and should have the correct voltage rating and current rating for the equipment it is protecting. It is also important to regularly check the fuses to ensure that they are functioning properly and that the metal strip has not been damaged.
In conclusion, electrical fuses are an important safety device that protects equipment from damage caused by over currents. They come in different types, each with their specific use, and it is important to ensure that the correct fuse is used for the specific application. Proper installation and maintenance of fuses can prevent equipment damage and fires, and it is important to follow the local electrical code when installing and maintaining fuses. Therefore, it is necessary to choose the right fuse with suitable characteristics such as voltage rating, current rating, and interrupting rating, to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.
Related Post: Fuse Characteristics: The Science Of Characteristics Of Fuse Wire In A Circuit
FAQs
A volt is a unit of measurement for electric potential difference or electric pressure. While a surge is a sudden increase in voltage in an electrical circuit.
An electrical connector may be surrounded by a fuse to protect the circuit from overloading, which can happen due to high currents or high faults. So, we can identify and clears a fault. A fuse can protect the load current to a maximum voltage which is different for each fuse and called rated voltage.
A fuse contains a fusible wire which is always low-resistance as compared to other appliances of the circuit. Due to this reason, it melts earlier in case of high interrupting current flow.
Sign Up




