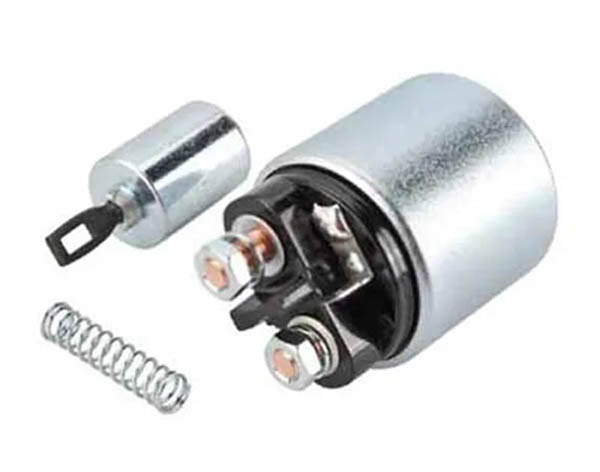
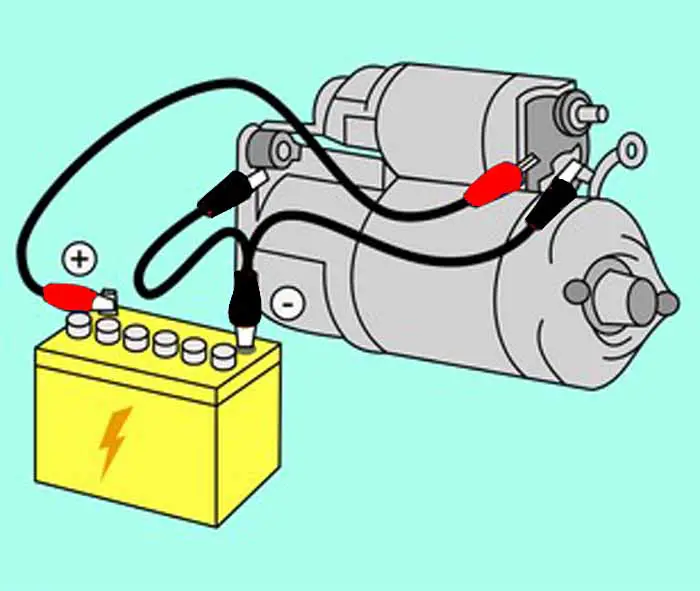
Many people get confused between the starter motor and the starter solenoid. The solenoid and motor are two different components.
The starter motor is the big cylindrical part that cranks the engine. While the solenoid is the small cylindrical component, which acts as a switch that connects and disconnects the motor assembly to the battery. If you want to know about the starter solenoid parts and function. This page is for you.
On this powerful page, you are going to learn the six starter solenoid parts, their functions, and work in comprehensive detail.
Related Post: 11 Parts Of Car Starter Motor & Functions
What is Starter Motor
The starter motor is a critical component of the car’s starting mechanism, and its proper functioning is essential for the engine’s operation. A vehicle’s starter motor is an electric motor responsible for initiating the engine’s operation. When the operator turns the ignition switch or starts button, the motor receives an electrical signal from the car’s battery, prompting it to rotate the engine’s flywheel.
The flywheel, in turn, initiates the engine’s crankshaft, which catalyzes the combustion process within the engine’s cylinders. Ordinarily, the starter motor will disengage automatically once the engine is operational. However, if the engine fails to start or stalls, the operator may need to re-engage the motor to restart the engine.
Related Post: How a Starter Motor Works: A Detailed Insight
Starter Solenoid:

A starter solenoid or starter solenoid switch is a cylindrical component used to activate and deactivate the starter motor assembly. It is an electromagnetic switch that connects and disconnects the car battery from the motor.

The starter solenoid is a small cylinder bolted on top of the starter motor assembly. A starter motor requires huge energy and a large amount of current is consumed. As a result, a larger starter control switch is needed to handle the high power flow, and this is where a solenoid comes into play. The solenoid is used to handle the high current flow required by the starter motor, allowing for efficient and reliable starting of the engine.
A solenoid is a huge switch, used to turn ON and OFF the starter motor assembly. The principle behind the solenoid is that a small current is used to turn on a bigger current. It acts as a bigger relay that energizes the control circuit of the starter.
Although, sometimes the starter has another relay for the solenoid in the fuse box to increase the current demand for the solenoid. But, the solenoid even acts as a bigger relay for the starter motor assembly to meet the high current demand.
Related Post: How To Wire A Starter Solenoid
What Is The Function Of The Starter Solenoid
The typical starter solenoid serves the following five functions:
- Acts as a relay that creates a heavy-duty path
- Pushes the starter pinion gear forward
- Holds the pinion gear engaged with flywheel teeth
- Retract the pinion gear back from the flywheel after starting
- Quickly turns ON and Off the starter motor to avoid damage
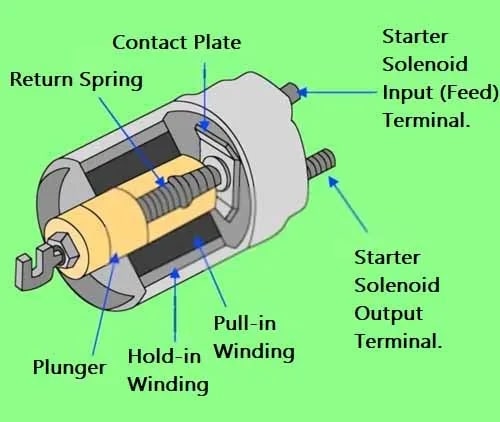
Starter Solenoid Construction
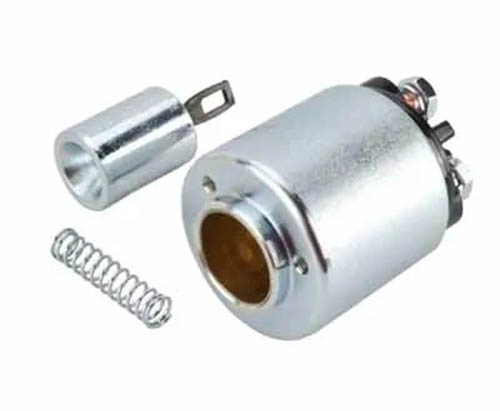

A starter solenoid consists of a movable rod called a plunger with a lever fork, two heavy-duty copper contact, a return spring, and two windings pull-in and hold-in windings.

It also has three terminals, one small terminal and two thicker, at the back of the solenoid cap. The small starter control terminal is for its control, you can call it the “S” terminal, which stands for “Signal”. To activate the solenoid, the ignition switch is turned on, which signals the “S” terminal for activating the solenoid.
The remaining two terminals are thicker and larger than the other terminal to the starter in which one terminal is the input terminal, which supplies power to the starter solenoid from the battery positive source. The second terminal is the output terminal and goes on to connect to the motor assembly.
Related Post: Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram
How A Starter Solenoid Works
The working principle of the solenoid is based on using the little current to switch ON a bigger current.
When the driver turns the key in the ignition, the current starts to flow via a thin cable from the switch to the fuse, to the starter relay, and finally to the ignition switch “S” terminal of the solenoid. The ignition switch “S” terminal is linked with two types of windings pull-in and hold-in windings in the solenoid.
When the current flows to these windings, it creates electromagnetism that pulls the plunger inside the starter, when this is pulled, two functions happen at the same time. One is the plunger moves forward the pinion gear by lever fork to mesh with the ring gear of the engine flywheel.
The second function is, it closes two heavy contacts present at the other end of the plunger which works as a bridge and connects the battery to the motor assembly. These two heavy closed contacts enable the current to flow from the solenoid to the starter motor assembly. As a result, the motor assembly begins to rotate and this rotation is then transferred to the engine flywheel by pinion gear.
And finally, the car is cranked.
Starter Solenoid Parts
In this section, we will discuss three parts of the starter solenoid and its functions and working.
- Solenoid Pull-in and hold-in winding
- Solenoid Plunger
- Solenoid Fork Lever
- Solenoid Cap
- Solenoid Return Spring
- Solenoid Contact Plate
1. Starter Solenoid Pull-In And Hold-In Winding:
A solenoid consists of two types of windings a strong pull-in winding and a weak hold-in winding. These winding are thicker copper wire loops wrapped around the rod. Together both windings, when activated, attract the plunger, and then the only hold-in winding is used to hold it in the closed position.
One end of both windings is connected to the battery-positive power source through the “S” terminal of the starter solenoid. The other end of the first hold-in winding is connected directly to the starter motor case. Conversely, the other end of the second pull-in winding is connected to the solenoid output terminal of the motor winding and then to the ground.
How Starter Solenoid Pull-In And Hold-In Winding Works
When the start key is turned ON, the current starts to flow to the pull-in and hold-in winding through the “S” terminal of the solenoid. These windings create electromagnetism that attracts the plunger inside windings, which enables the meshing of the pinion gear with the flywheel ring gear, at the same time, it makes the connection between the battery and the motor.
As the plunger moves, it also causes the pull-in winding to stop the flow of current. This is because when it moves the starter motor gets current, and the second end of the pull-in winding is connected to the starter motor. And there is a live current on both sides of the pull-in winding and no ground is present.
The reason is, it takes a lot more energy to pull the plunger from outside than it does to hold it there. The hold-in winding still has power because it is grounded to the motor case. Once the pinion gear meshes with flywheel teeth, it is no longer necessary to power the pull-in winding, and it will only create a burden on the battery. So, the only necessary winding to power is the hold-in winding, it keeps the rod attracted. At this time the motor is activated which cranks the flywheel until the engine starts and the key is released.
Function Of Solenoid Pull-In And Hold-In Winding
The function of both windings is to move the plunger forward and hold it there.
2. Solenoid Plunger

The plunger is a movable rod located inside the winding held by a return spring. At one end of it, the lever fork is attached, which causes the back-and-forth movement of the pinion gear when the solenoid is turned on and off.
At the other end, it has two copper contacts, which when completes its journey, make heavy connections between the battery and the starter motor armature. When current flows to the solenoid, the pull-in, and hold-in windings are energized, this creates an electromagnetic field that moves the plunger.
Function Of The Plunger
The function of the plunger engages and disengages the pinion gear with the flywheel and at the same time closes and opens two heavy contacts from the battery to the starter motor assembly.
3. Solenoid Fork Lever
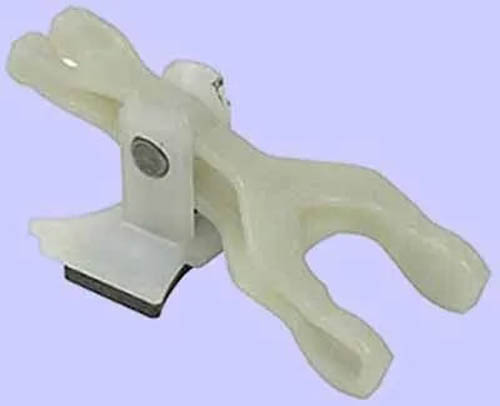

It is a fork-shaped lever that connects the starter solenoid with the overrunning clutch in the starter motor. It is used to develop a forward and backward movement of the pinion gear to mesh and de-mesh with the engine flywheel ring gear.
Construction Of The Solenoid Fork Lever
A fork lever is a fork-shaped lever, manufactured from metal or plastic (Nylon) material. One end of the fork lever is connected to the plunger and the other end of it is connected to the overrunning clutch.
Function Of The Solenoid Fork Lever
The function of the fork lever is to create back-and-forth movement of the pinion gear to connect and disconnect with the flywheel ring gear.
Working Of Solenoid Fork Lever
The lever fork works on the principle of the lever which pushes out the pinion gear when the other end is pushed in opposite direction. When the solenoid is activated, it moves the plunger which also moves the lever fork that pushes out the pinion gear at the other end
4. Solenoid Cap

The starter solenoid end is covered up with the solenoid cap. It is the end part of the solenoid. The solenoid contains terminals. It has three terminals, one small ignition switch terminal, and two heavy terminals.
The small “S” terminal is connected to an ignition switch which activates when the driver turns the key to the start position and deactivates when the driver releases the key. The two other terminals are heavy terminals that create the connection between the battery and the starter motor when the solenoid is activated.
The Function Of Solenoid Cap
The function of the starter solenoid cap is to hold the starter terminals and allow them to complete the starter circuit.
5. Solenoid Return Spring

The starter solenoid return spring is attached to the plunger, which restores the plunger to its original resting position. When the key is turned, the solenoid is energized and the plunger is pulled due to electromagnetism to move the pinion gear to turn the flywheel.
Conversely, when the driver releases the key and the solenoid de-energizes, so the plunger remains in the pulling position if the return spring would not present. With the help of the return spring, the plunger pulls back to its original resting position.
Function Of The Solenoid Return Spring
The function of the return spring is to bring back the plunger to its original resting position after the end of the starter solenoid operation.
6. Solenoid Contact Plate

This is a plate-type starter solenoid component, placed at end of the plunger. It creates connections between two heavy contacts with solenoid cap terminals when the solenoid is energized and the plunger is pulled. It works as a bridge by making the connection with solenoid cap terminals to allow the current to pass from the battery to the starter motor assembly.
Function Of The Contact Plate
The function of the starter solenoid contacts plate is, it completes the starter motor circuit by bridging the solenoid cap terminals.
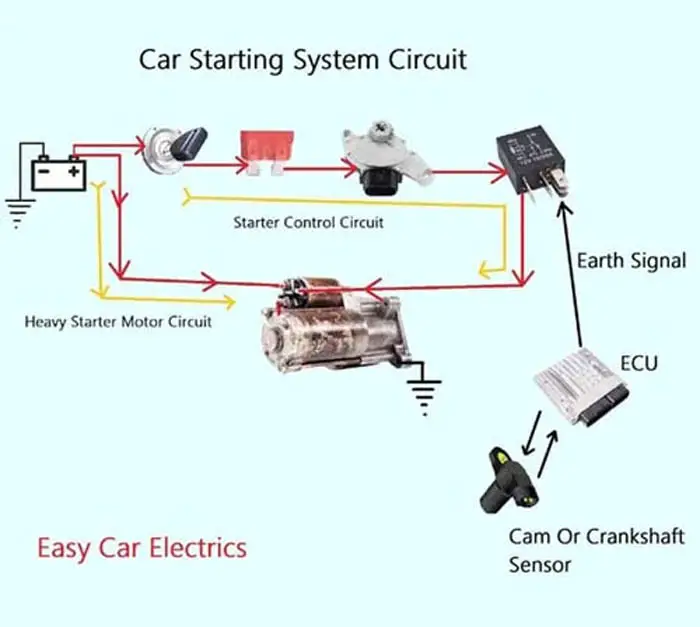
Related Post: Car Starting System, Diagram, Working, Components, Function
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A starter solenoid engages the starter motor in an internal combustion engine. The solenoid consists of a coil of wire that is wrapped around an iron core. When electricity is applied to the solenoid coil, it creates a magnetic field that pulls the armature toward the center of the solenoid. This action causes the starter motor to turn, which then begins the engine.
When a solenoid fails in the car starter motor, the engine will not start. The solenoid is responsible for providing the electrical current to the starter motor, which then starts the engine. without the solenoid, the starter would not function and the engine will not start.
Some common symptoms of a bad starter include a clicking noise, the gear and starter not engaging properly, and the starter motor failing to turn over.
The circuit of the starter is the electrical system that powers the starter motor. It is important because if any part of the circuit is damaged or not functioning properly, it can prevent the starter motor from working and prevent the engine from starting.
The part that connects the ignition key to the starter motor is called the starter control wire. This wire is responsible for transmitting the electrical signal from the start key to drive the starter motor, which enrolls the starter gear and begins turning the engine.
Yes, a bad starter solenoid can cause problems with the starter. When the solenoid receives an electrical signal from the start key, the starter solenoid closes and the solenoid pushes the starter drive to enroll the starter gear and turn the engine. If the solenoid is not functioning properly, it may not receive the signal or it may not be able to close and push the starter drive, which can prevent the engine from starting. In some cases, solenoid problems may require to replace a starter solenoid.
Sign Up